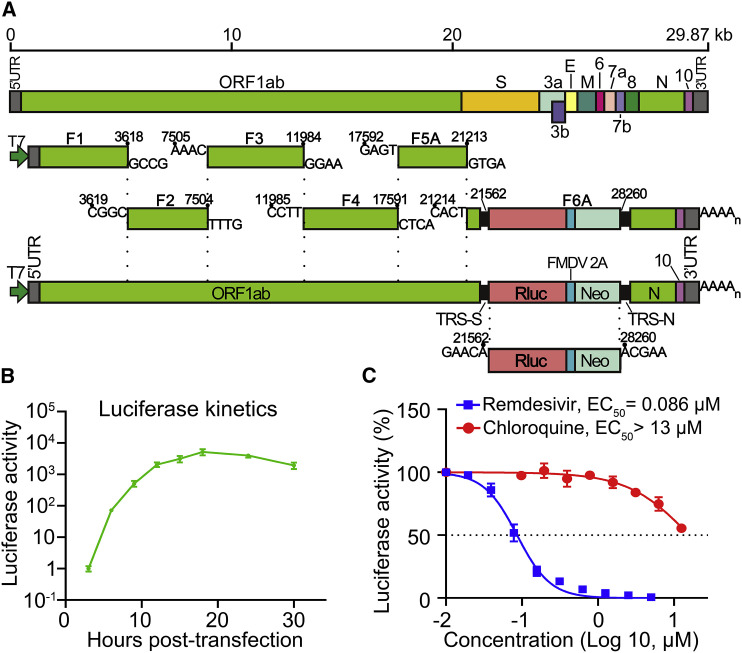
Figure 5.
A SARS-CoV-2 Luciferase Replicon
(A) Construction of SARS-CoV-2 luciferase replicon. The replicon was constructed by deleting nucleotides 21,563–28,259 from the SARS-CoV-2 genome. The deleted viral segment was replaced by a Rluc, a foot-and-mouth disease virus 2A (FMDV 2A), and a neomycin phosphotransferase (Neo). The Rluc/FMDV 2A/Neo reporter is under the control of transcription regulatory sequence (TRS) of the deleted S gene. Replicon cDNA was assembled by six contiguous cDNA fragments through in vitro ligation. Replicon RNA was in vitro transcribed.
(B) Replicon luciferase assay. Huh-7 cells were co-electroporated with replicon RNA and N-encoding mRNA (20 μg), seeded into a 48-well plate, and assayed for Rluc activities at indicated time points.
(C) Antiviral testing of remdesivir and chloroquine. Huh-7 cells, electroporated with replicon RNA from (B), were seeded into a 96-well plate (50 μL per well), treated with compounds (50 μL per well) for 24 h, and quantified for Rluc activities. The DMSO control treatment was set to 100%. Data are mean ± SD from three independent experiments. EC50 values were calculated by nonlinear regression.