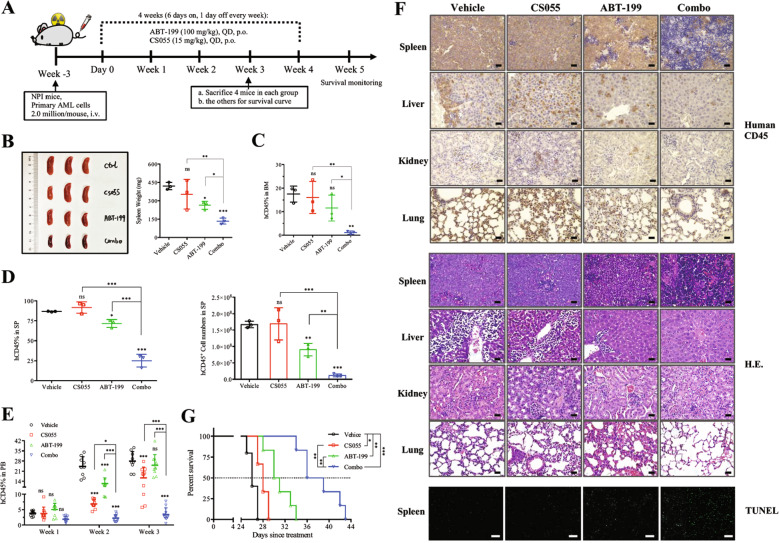
Fig. 7. The ABT-199/CS055 combination regimen is highly active in vivo in a PDX mouse model generated from an acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patient carrying FLT3-ITD mutation.
a The scheme for the process of the experiments using a PDX mouse model generated by tail vein injection of NOD-Prkdc−/−IL2rg−/− mice with cells obtained from a patient carrying FLT3-ITD (#13 as shown in Supplementary Table S2). Three weeks after cell inoculation, mice were randomly assigned into four groups and received vehicle, CS055 (15 mg/kg), ABT-199 (100 mg/kg), or the combination by oral gavage for four consecutive weeks by following a weekly schedule of 6 days on and 1 day off. b Images of spleens removed from three representative mice were shown (left), and the weight of the spleens was measured (right). c–e Flow-cytometric analysis was performed to determine tumor burden of human CD45+ leukemic cells in femur bone marrow (BM; c), and spleen (SP; d, left— percentage and right—absolute number of human CD45+ leukemic cells). e Flow-cytometric analysis was performed to monitor the percentage of human CD45+ leukemic cells in peripheral blood (PB) every week. f Immunohistochemical staining for human CD45 (upper) and H&E staining (middle) were performed to examine infiltration of tumor cells in the spleen, liver, kidney, and lung (scale bar: 25 µm). Alternatively, TUNEL staining was performed to visualize apoptotic cells in the spleen (bottom; scale bar: 100 µm. g Kaplan–Meier analysis was performed to assess animal survival (**P < 0.01).