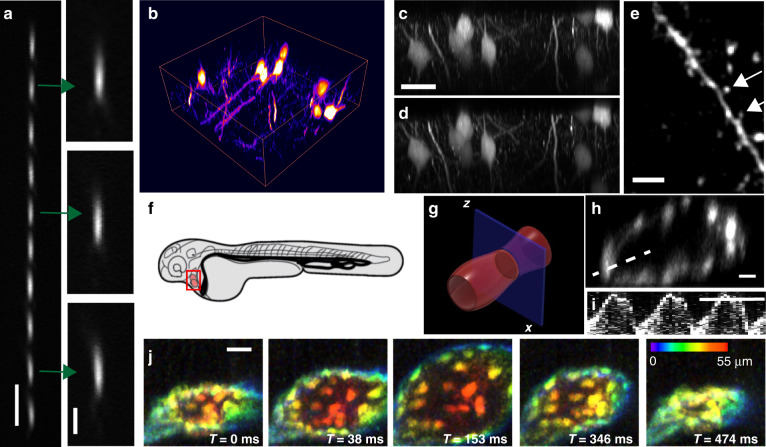
Fig. 5. Two-photon microscopy with resonant axial remote focusing.
a Point spread function using 200 nm fluorescent nanospheres moved to different axial positions, acquired via resonant (12 kHz) remote focusing with a tilted planar mirror (5° tilt). b Rendering of a fixed brain slice labelled with Thy1-GFP acquired using resonant remote focusing. c Axial XZ view of the brain slice shown in b using remote focusing. d Axial XZ view of the same brain slice but acquired with conventional Z-stepping. e Lateral XY view of the brain slice shown in b, acquired with resonant remote focusing. Arrows mark individual spines. The image was convolved with a Gaussian filter (sigma = 1 pixel) to suppress spurious noise. f Schematic drawing of a zebrafish embryo. g Zoomed-in view of the zebrafish heart. The blue plane depicts the axial imaging plane. h Averaged (over 30 cycles) XZ cross-section of the zebrafish heart labelled with Tg(kdrl:EGFP), acquired with a frame rate of 45 Hz. i Kymograph of the beating heart measured along the line shown in h. The kymograph uses raw data, and no averaging was applied. j Volumetric imaging of the zebrafish heart at a volume rate of 156 Hz, XY view with depth encoded in colour. Scale bars: a and e: 5 µm; a (inset): 2 µm; c, h, and j: 20 µm; i: 0.5 s