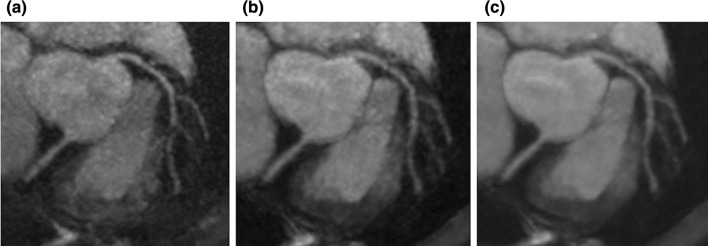
Fig. 5.
Coronary MRA images of PI, CS, and CS with deep learning reconstruction. Three MPR images with identical resolution yet different image acceleration methods and post-processing are shown. a PI. b CS. c CS with deep learning reconstruction postprocessing. c The best image quality among the three images. The PI and CS images were acquired with a spoiled gradient echo sequence with ECG-gating, diaphragm navigator gating, and fat suppression with spectral attenuated inversion recovery. The MRI acquisition parameters were FOV = 380 × 380 mm, Matrix = 392 × 384, slice thickness = 1.0 mm, slice number = 152, acceleration factor = 2.0 × 2.0, TR = 5.3 ms, TE = 2.0 ms, flip angle = 12 degree, bandwidth = 279 Hz/pix, acquisition voxel size = 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 mm, reconstructed voxel size = 0.5 × 0.5 × 0.5 mm, navigator gating window = 4 mm. For the DLR technique, see Refs. [116, 140]. MRA magnetic resonance angiography, PI parallel imaging, CS compressed sensing, MPR multiplanar reconstruction