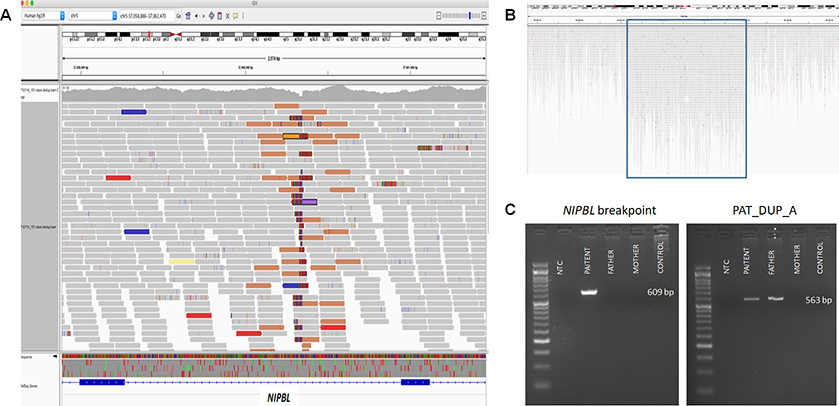
Figure 2. Whole genome sequencing data and PCR amplification of NIBPL breakpoint and of paternally inherited duplication.
(A) Screenshot of whole genome sequencing (WGS) data showing breakpoint junction region disrupting NIPBL. (B) Screenshot of WGS data indicating duplication of chromosome 1: 69,063,596–69,119,765 [hg19]. (C) Breakpoint junction analysis of der6_jct1, interrupting NIPBL, indicated that the rearrangement occurred de novo in the proband (left panel). Amplification of der7_jct1 (between segments 6–16 and the duplication on chromosome 1) indicated that the duplication on chromosome 1 was inherited from the father, and presumably moved en bloc with segment 6–16 during formation of the complex rearrangement (right panel).