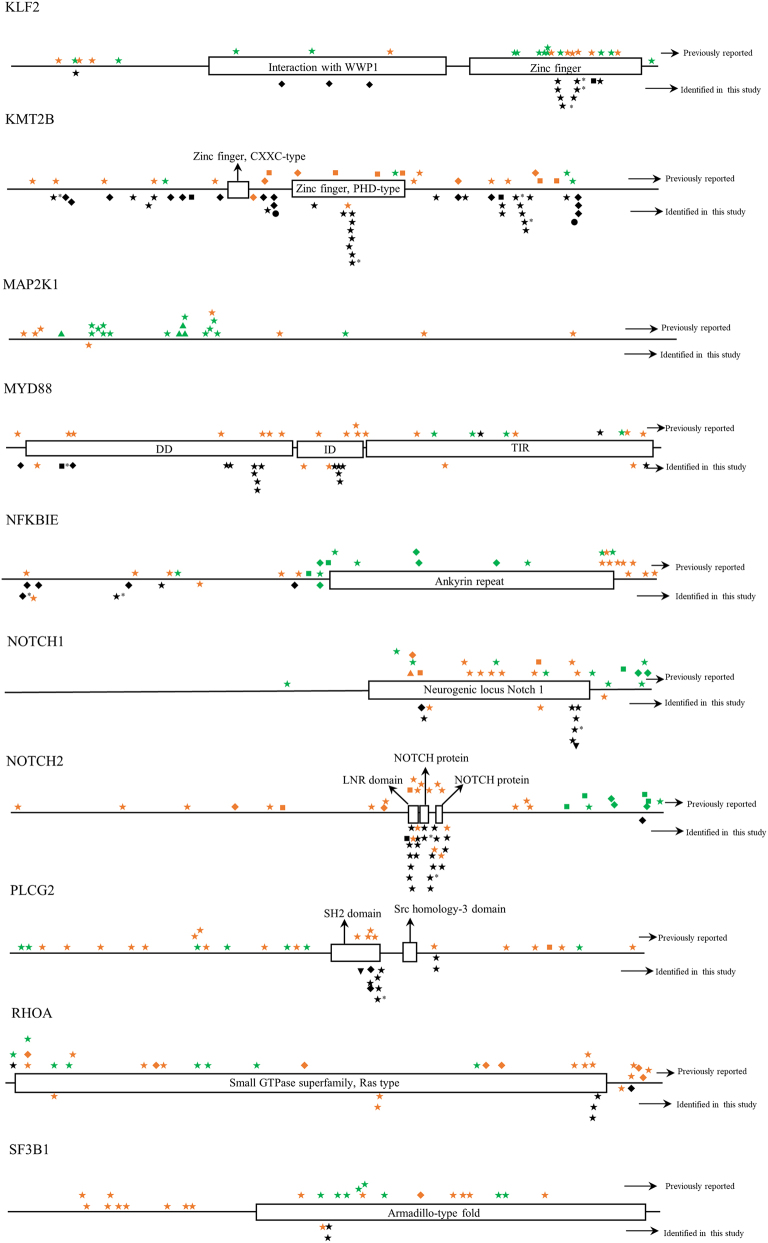
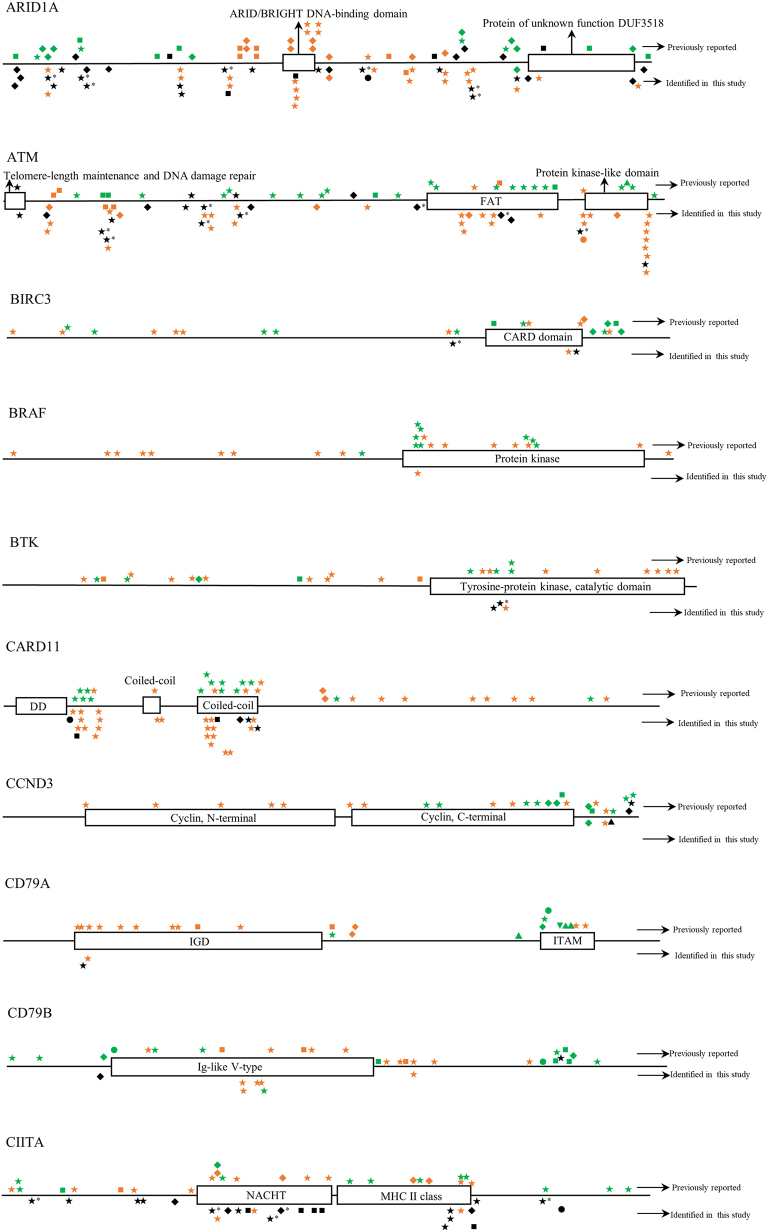
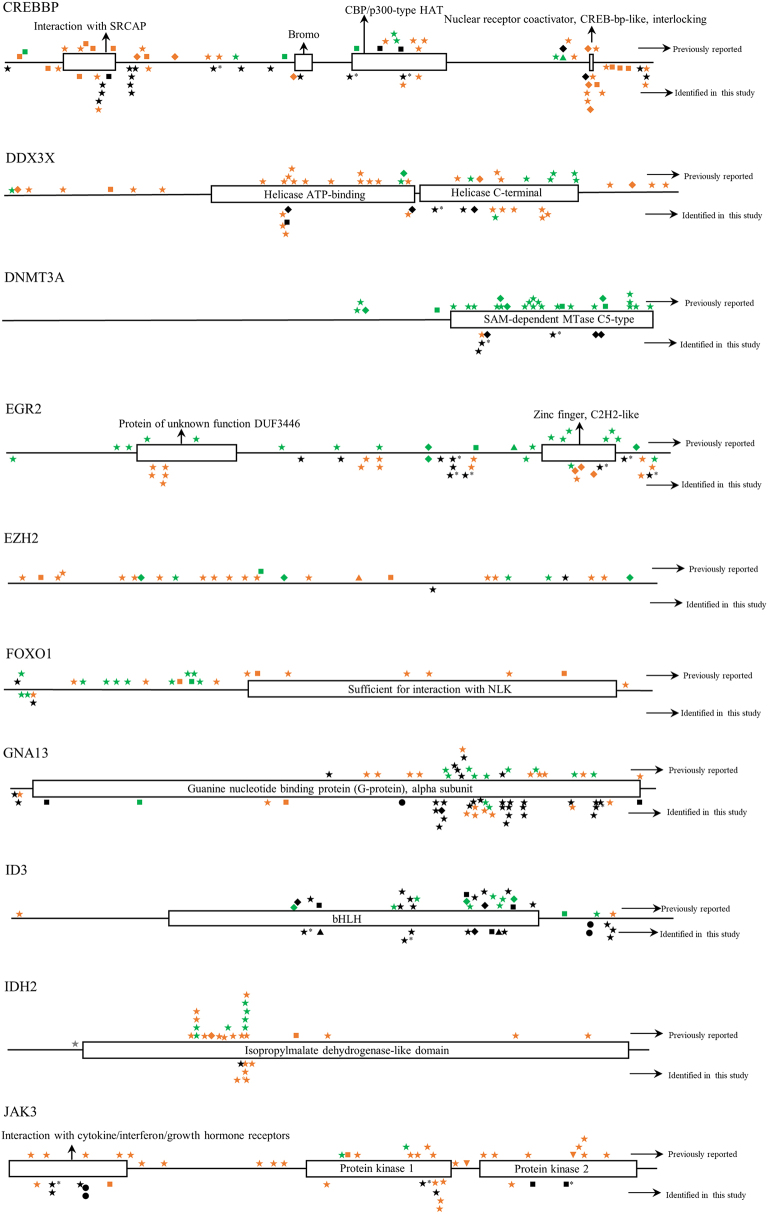
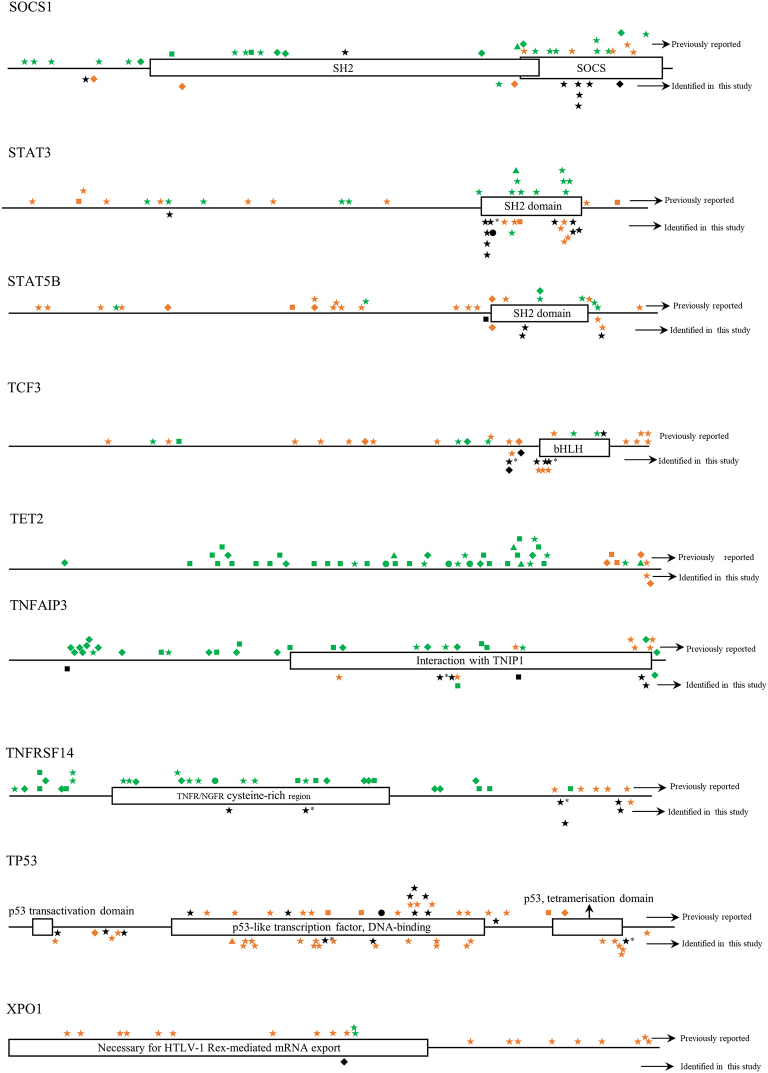
Fig. S1.
The distribution of mutations identified in each gene in childhood Burkitt lymphoma cases of this study. Dark shapes represent the mutations detected in Burkitt lymphoma; green shapes represent the mutations detected in other lymphomas; orange shapes represent the mutations detected in diseases other than lymphoma. *, mutations belong to single nucleotide polymorphism; ◆, frameshift mutation; ▼, insertion mutation; ▲, deletion mutation; ★, missense mutation; ■, nonsense mutation; ●, splice site or untranslated region mutation; FAT, focal adhesion targeting; CARD, caspase recruitment domains; DD, death domain; IGD, Ig-like domain; ITAM, immuno-receptor tyrosine-based activation motif; NACHT, NAIP, CIITA, HET-E, and TP1; bHLH, basic helix-loop-helix; ID, linker domain; TIR, Toll-IL-1 receptor; LNR, Lin12/Notch related; SH2, Src homology domain; SOCS, suppressor of cytokine signaling.