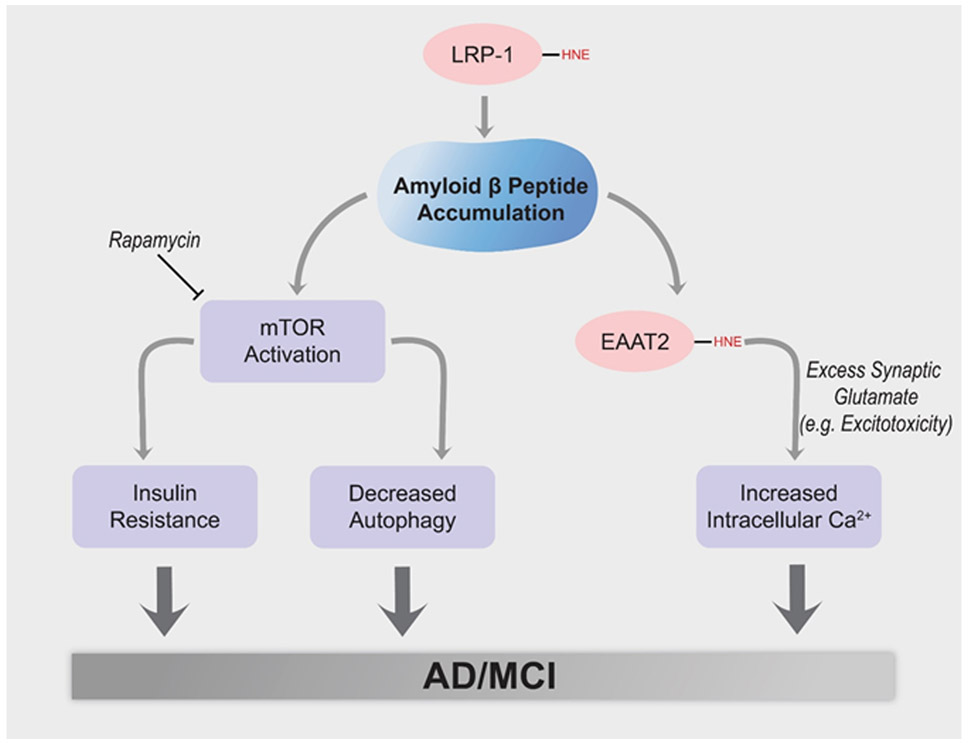
Figure 5.
Aβ42 oligomer-associated lipid peroxidation leads to inhibition of the low density-like receptor protein-1 (LRP-1), whose loss of function could contribute to brain accumulation of Aβ42 and resulting oxidative damage. In addition, Aβ42 oligomers are reportedly capable of initiating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis, with resulting insulin resistance and inhibition of autophagy. Similarly, Aβ42 oligomer-associated lipid peroxidation leads to HNE binding to and inhibition of the glutamate transporter, EAAT2 (also called Glt-1) in AD brain, likely contributing to excitotoxicity and neuronal death.