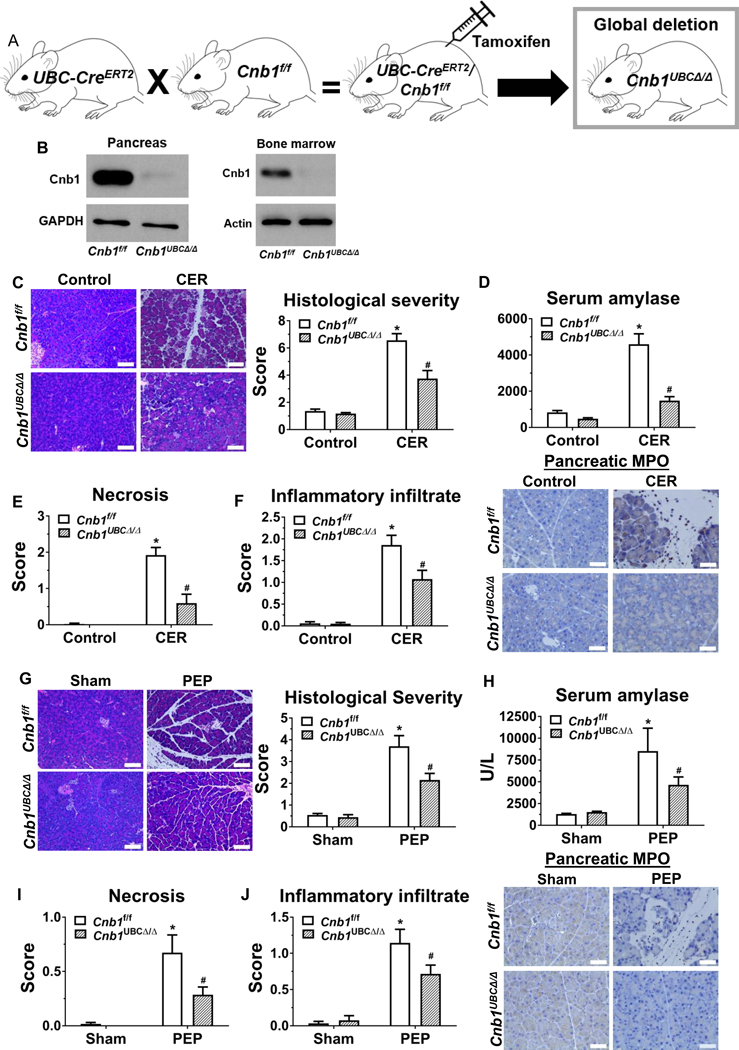
Figure 5. Global deletion of CNB1 protects against two disparate models of acute pancreatitis.
(A) The global Cnb1 conditional knockout line (Cnb1UBCΔ/Δ) was induced by crossing UBC-CreERT2 mice with Cnb1f/f mice, followed by tamoxifen administration. (B) Western blotting confirms negligible Cnb1 expression in the pancreas and BM cells from the Cnb1UBCΔ/Δ mice. (C) Representative H&E images of the pancreas (200X) from the control and CER conditions from Cnb1f/f and Cnb1UBCΔ/Δ mice and overall histological severity scoring. (D) Serum amylase. (E) Subscoring for necrosis. (F) Subscoring for inflammatory infiltrate and immunostaining for pancreatic myeloperoxidase (MPO) (400X). (G) Representative H&E images of the pancreas (200X) from the sham and PEP conditions from Cnb1f/f and Cnb1UBCΔ/Δ mice and overall histological severity scoring. (H) Serum amylase. (I) Subscoring for necrosis. (J) Subscoring for inflammatory infiltrate and immunostaining for pancreatic MPO (400X). n=5 animals per conditions; *p<0.05, compared to the controls; #p<0.05, compared to the Cnb1f/f condition.