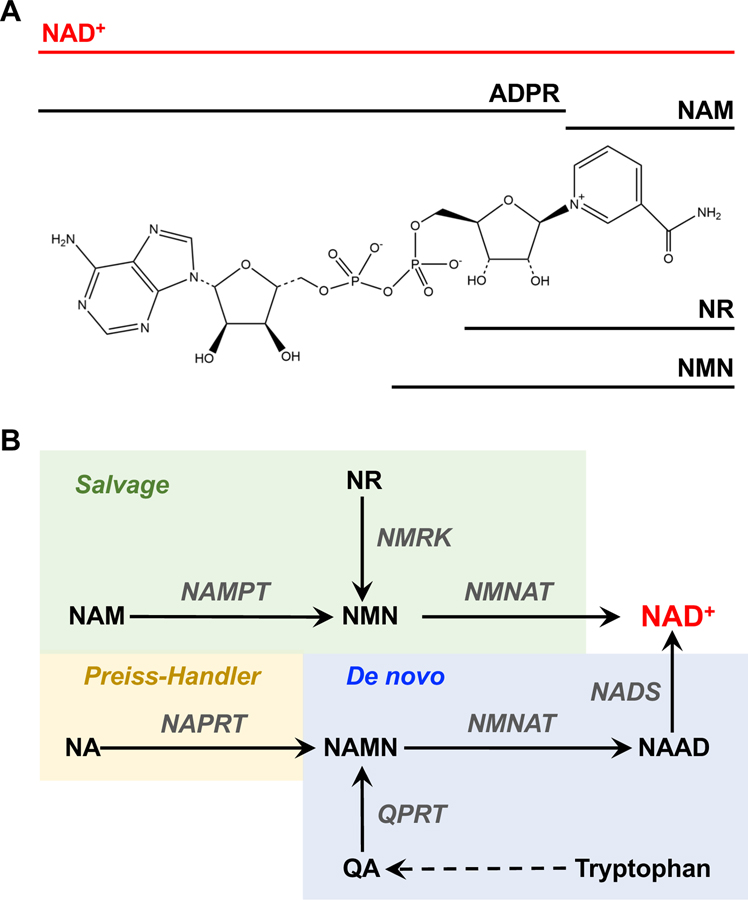
Figure I. Chemical Structure and Biosynthesis of NAD+.
(A) Chemical structure of oxidized NAD+. NAD+ comprises two nucleotides, one containing an adenine nucleobase and the other containing nicotinamide, joined through their phosphate groups. The location of various chemical moieties contained within NAD+ are indicated: ADP-ribose (ADPR), nicotinamide (NAM), nicotinamide riboside (NR), and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). (B) NAD+ is synthesized de novo in a pathway leading from tryptophan (blue), as well as in ‘salvage’ pathways: (i) the nicotinic acid (NA) (‘Preiss–Handler’) salvage pathway (yellow), (ii) the nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) salvage pathway (green), and (iii) the nicotinamide riboside (NR) salvage pathway (green). The abbreviations for the enzymes (gray text) and the intermediates (black plain text) are defined in Table 1.