Fig. 3. Lipoproteins are PM20D1 co-activators in vitro and in vivo.
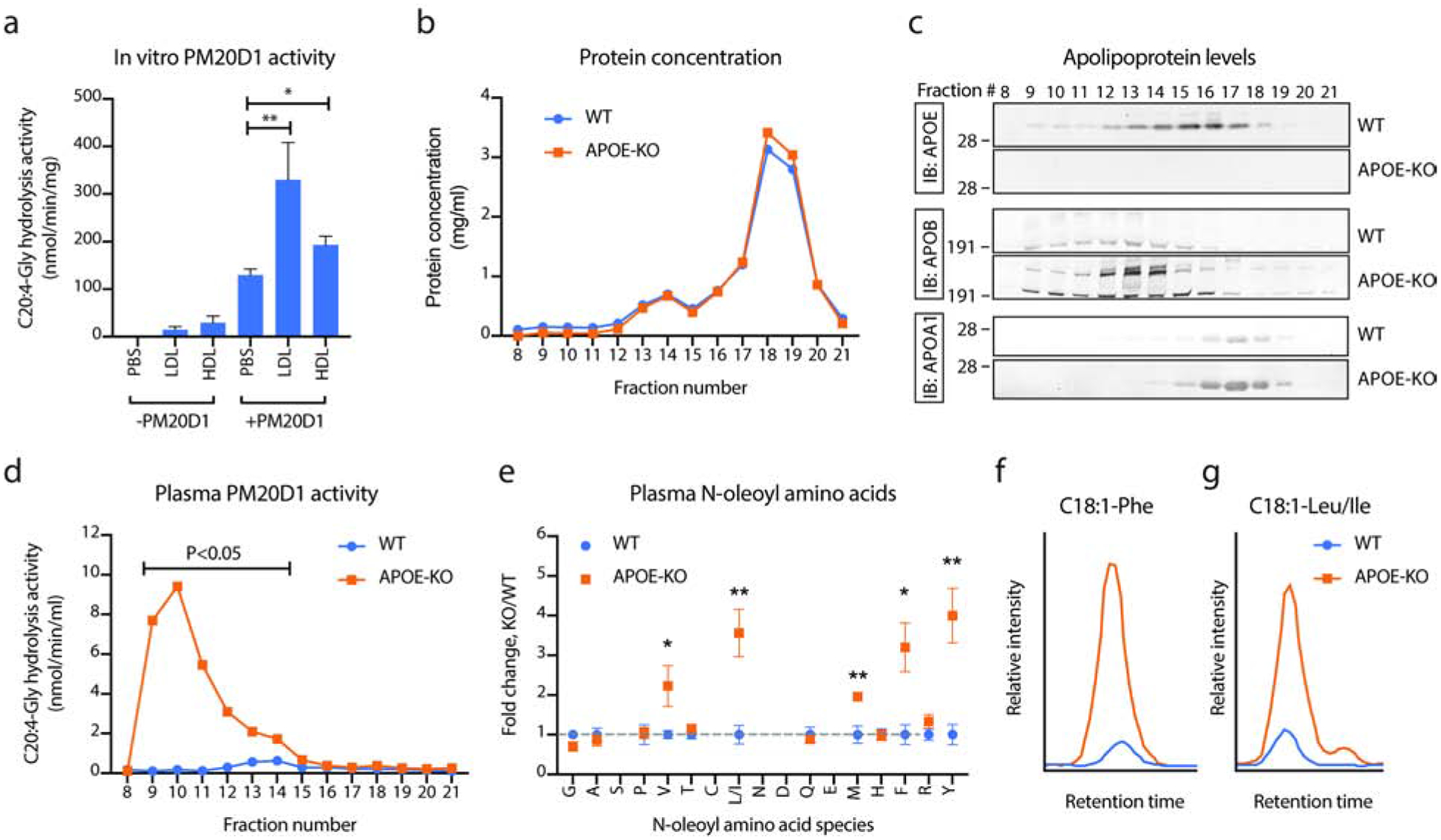
(a) C20:4-Gly hydrolysis activity of mammalian recombinant, purified mouse PM20D1 (0.1 ug/reaction) alone or following incubation with APOB+ or APOA1+ lipoproteins (LDL and HDL, respectively) isolated from PM20D1-KO mice. N=5/group.
(b-d) Protein concentrations (b), apolipoprotein levels (c), and PM20D1 activity as measured by C20:4-Gly hydrolysis activity (d) of fractionated mouse plasma from either WT (blue trace) or APOE-KO (orange trace) mice.
(e) Total plasma N-acyl amino acid levels from WT (blue) or APOE-KO (orange) mice. N=5/group.
(f,g) Representative LC-MS traces of C18:1-Phe (f) and C18:1-Leu/Ile (g) from WT (blue) or APOE-KO (orange) mice.
For (a), LDL or HDL was isolated from plasma of five pooled PM20D1-KO mice. For (b-d), plasma from five mice per group was pooled together and separated by fast protein liquid chromatography-size exclusion (FPLC-SEC). For (e), N=5/group.
For (a), (d), and (e), Student’s two-tailed t-test was used for the indicated comparison or for WT versus APOE-KO mice. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01. Data are shown as means ± SEM. See also Table S3 and S4.
