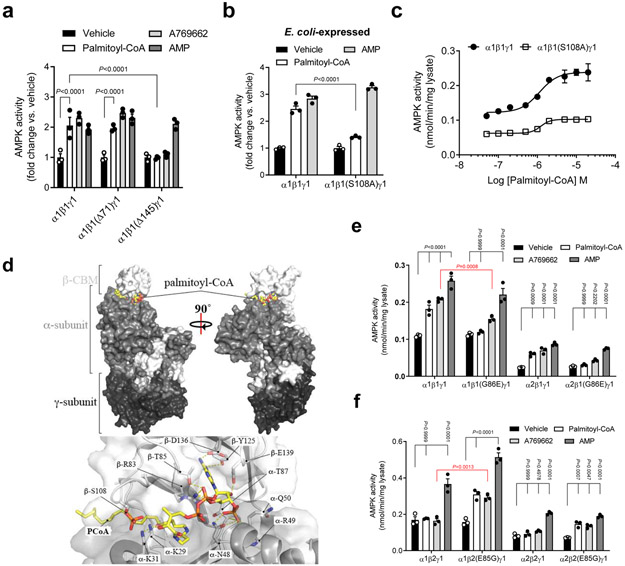
Figure 2. LCFA-CoA activation is mediated through the AMPK ADaM site.
a, Activities of AMPKα1β1γ1 (WT or N-terminal deletions of β1 residues 1-71 (Δ71) or 1-145 (Δ145)) ± palmitoyl-CoA (10 μM) or AMP (100 μM). b, c, Activities of AMPKα1β1γ1 (WT or β1S108A) ± palmitoyl-CoA (10 μM) or AMP (100 μM) (b) or increasing concentration of palmitoyl-CoA (c). For a, b, data are shown as mean fold change in activity vs. vehicle ± s.e.m.; n = 3. For c, data are shown as mean specific activity ± s.e.m.; n = 3. Statistical significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. n represent biological independent experiments. d, In silico modelling of palmitoyl-CoA bound to AMPKα2β1γ1. e, f, Activities of AMPKα1β1γ1 and α2β1γ1 (WT or β1G86E) (e), or AMPK α1β2γ1 and α2β2γ1 (WT or β2E85G) (f) ± palmitoyl-CoA (10 μM), A769662 (10 μM) or AMP (100 μM). Data are shown as mean specific activity ± s.e.m.; n = 3. Statistical significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test, or unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test (red P values). n represent biological independent experiments. Activities determined by 32P SAMS peptide assay. COS7 cell-expressed AMPK immobilized on anti-myc agarose was used in all experiments unless indicated.