Fig.4. CD133+Exo treatment decreases cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis while increasing myocardial capillary density in T2DM-stroke mice.
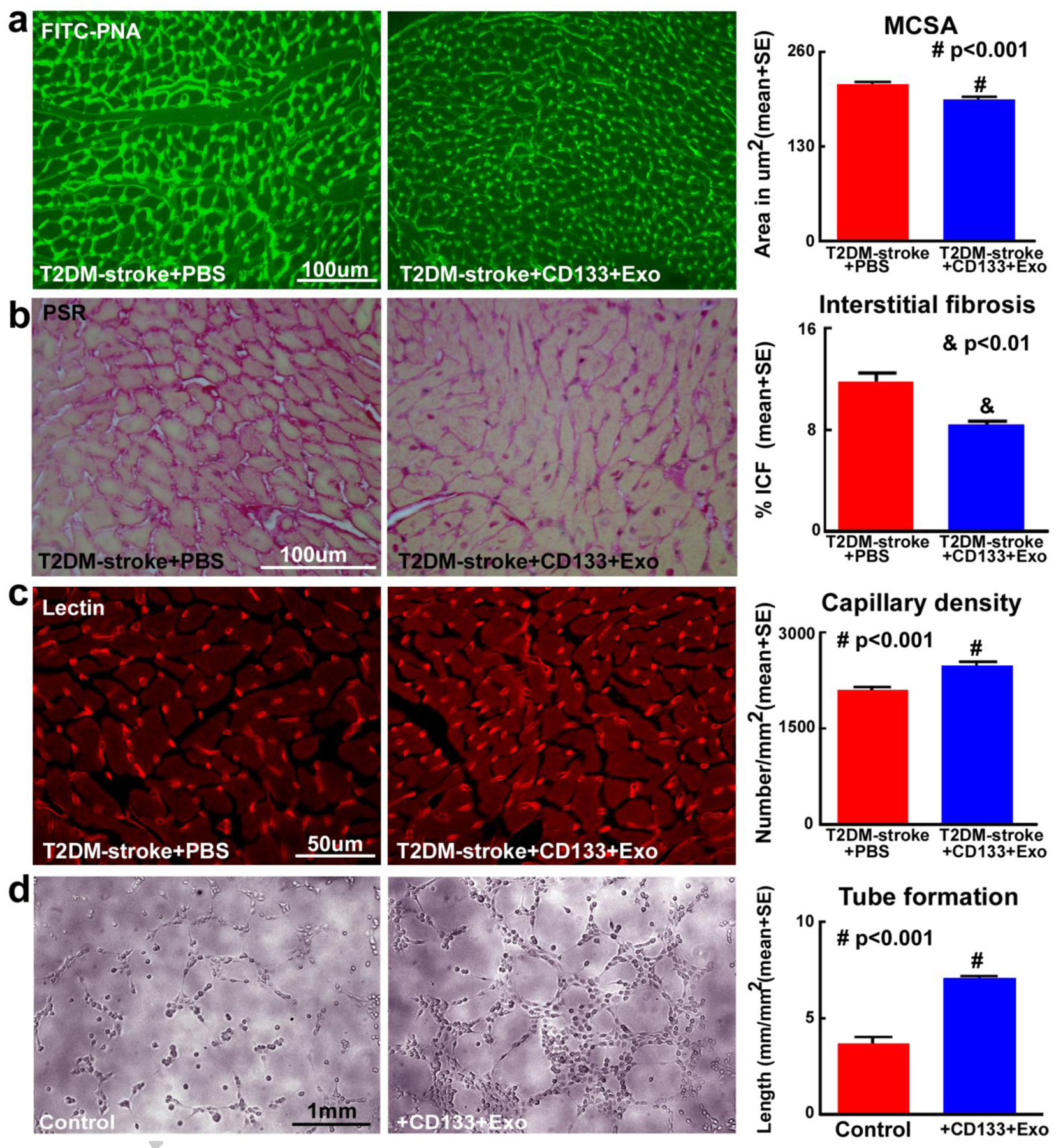
a) CD133+Exo treatment significantly decreases cardiomyocyte cross section area (MCSA) compared to PBS treated T2DM-stroke mice, indicated by FITC-Peanut agglutinin (FITC-PNA) immunostaining and quantification analysis. b) CD133+Exo treatment of T2DM-stroke mice significantly decreases interstitial fibrosis in the heart indicated by decreased interstitial collagen fraction (ICF) in PicroSirius Red (PSR) immunostaining. c) CD133+Exo treatment significantly increases myocardial capillary density compared to PBS treated T2DM-stroke miceindicated by Rhodamine-labeled Griffoniasimplicifolia lectin (lectin) immunostaining and quantification analysis. T2DM-stroke+PBS: n=7; T2DM-stroke+CD133+Exo: n=8. d) In-vitro, CD133+Exo treatment significantly increases capillary tube formation of mouse brain endothelial cells compared to media control.
