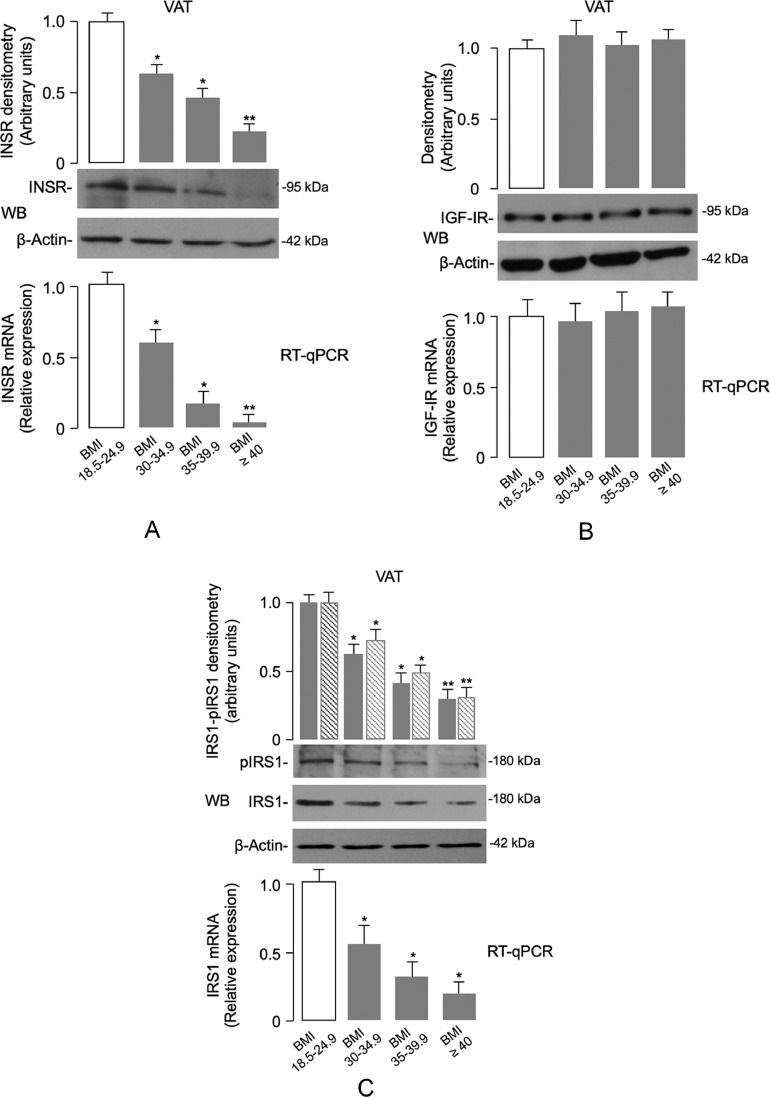
Fig. 1.
INSR, IGF-IR and IRS1 expression in human VAT. (A) INSR mRNA and protein levels from the normal-weight and obese individuals were measured by real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and Western blot (WB), respectively. The pattern of INSR mRNA and protein expression is shown in VAT samples from subjects in each BMI category (BMI 18.5–24.9 = 20 normal-weight subjects; BMI 30–34.9 = 7 obese subjects; BMI 35–39.9 = 8 obese subjects; BMI ≥ 40 = 11 obese subjects). A representative WB is shown. β-actin was employed as a control of protein loading. Densitometric scanning of INSR protein signals are shown in bar graphs. Levels of mRNA were normalized to RPS9 mRNA. Results are shown as mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05 vs normal-weight subjects; **P < 0.05 vs normal-weight subjects and vs individuals with BMI 30–34.9 [Student's t-test]. (B) IGF-IR mRNA and protein levels were measured as in (A), in VAT from normal-weight subjects and obese individuals. Bars represent the means of RT-qPCR and densitometric analysis of WB results from individuals in each BMI category. (C) Quantification of IRS1 mRNA and protein in VAT samples from subjects in each BMI category was as in (A). Densitometric scanning of total IRS1 (gray bars) and phosphorylated IRS1 (dashed bars) bands from representative WBs is shown. *P < 0.05 vs normal-weight subjects; **P < 0.05 vs normal-weight subjects and vs individuals with BMI 30–34.9 [Student's t-test].