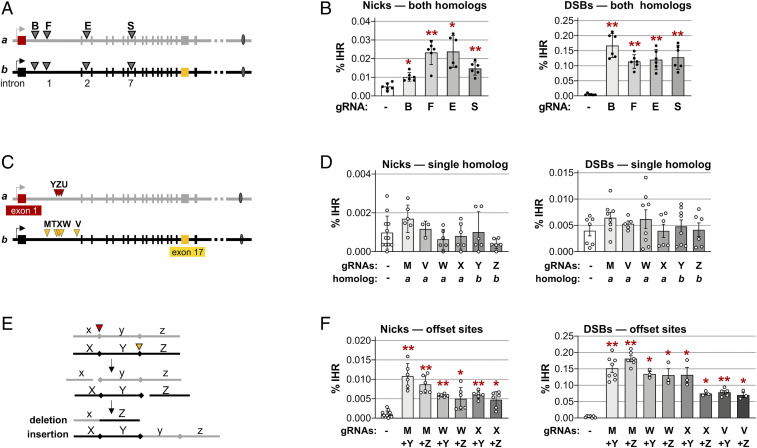
Fig. 2.
IHR joins offset nicks and DSBs. (A) Map of sites in introns 1, 2, and 7 of the CD44 gene targeted by gRNAs B, F, E, and S. (B) Frequencies of IHR in HT1080-K1 cells in which nicks or DSBs were targeted to both homologs by transfection of plasmids expressing Cas9D10A or Cas9 and no gRNA (-) or the indicated gRNA. Control cells were transfected with expression constructs for gRNA only, not enzyme. IHR frequencies are shown as mean and SD (n = 6); asterisks indicate significant differences from the no-gRNA control (*P < 0.05 and **P < 10−3). (C) Map of sites in CD44 targeted on only a single homolog by gRNAs Y, Z, or U (homolog a; red arrowheads) or M, T, X, W, or V (homolog b; gold arrowheads) in the engineered CD44-/- gene in HT1080-K2 cells. Sequences are shown in SI Appendix, Fig. S3. (D) Frequencies of IHR in HT1080-K2 cells in which nicks or DSBs were targeted to sites on a single homolog by transfection with an expression clone for Cas9D10A or Cas9, respectively, and no gRNA (-) or the indicated gRNA. IHR frequencies are shown as mean and SD (n ≥ 3). No IHR frequencies were significantly different from the no-gRNA control. (E) Diagram of recombinants predicted to result from the joining of ends of offset DSBs. Adjacent regions x, y, and z on the upper homolog (gray) and X, Y, and Z on the lower homolog (black) are cleaved at offset sites indicated by red arrowheads on either side of the central fragment, which has caps at its boundaries. Interhomolog EJ generates one recombinant in which region y is deleted and one in which it is inserted. See also Fig. 5A. (F) Frequencies of IHR at nicks and DSBs targeted to the indicated offset sites on the two homologs in HT1080-K2 cells by transfection with an expression clone for Cas9D10A or Cas9, respectively, and no gRNA (-) or the indicated gRNA. IHR frequencies are shown as mean and SD (n ≥ 3); asterisks indicate significant differences from the no-gRNA control (*P < 0.05 and **P < 10−3).