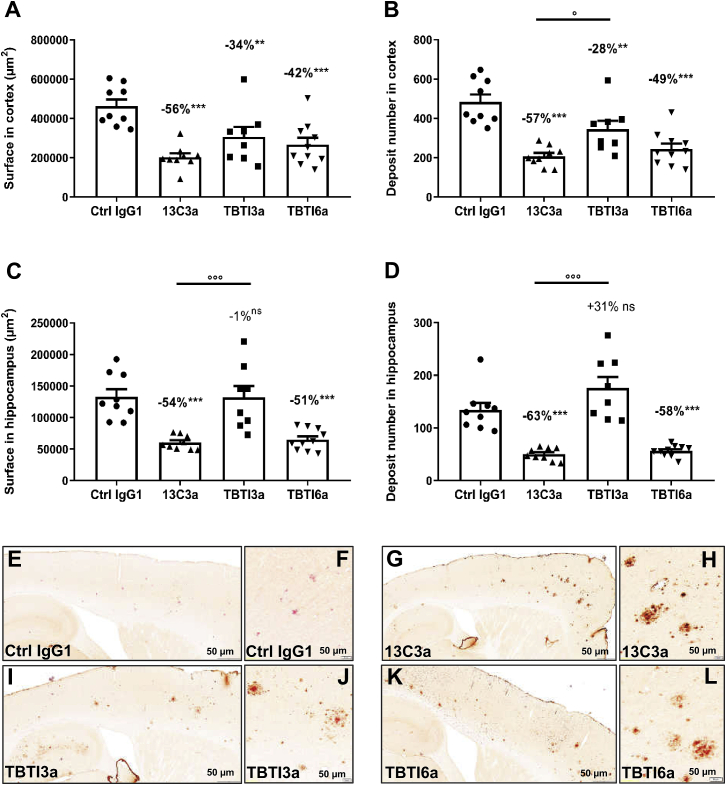
Figure 7.
Aβ Load and IgG1 Immunostaining in the Cortex and Hippocampus of APPSL Mice Treated with 13C3a and TBTI Antibodies
Quantitative analysis of Aβ immunostaining (4G8) in the cortex and hippocampus of APPSL mice after chronic administration of anti-Aβ (13C3a, 70 nmol/kg) or bispecific anti-Aβ/anti-TfR antibodies (TBTI3a and TBTI6a, 15 nmol/kg). Total surface and deposit numbers in the cortex (A and B) and hippocampus (C and D) over 8 cortical rostro-caudal anatomical levels. Data are means ± SEM. % calculated as means vs Ctrl IgG1. Statistics: one-way ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls post hoc analysis on raw data (for cortex, A and B) or on Log-transformed data (for hippocampus, C and D). ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus Ctrl IgG1. °p < 0.05, °p < 0.001 versus 13C3a. Representative images of cortical and hippocampal subareas of sagittal hemibrain sections immunostained with anti-IgG1 antibody and counterstained with Congo red of APPSL mice administered once a week for 4 months with Ctrl IgG1 (E), 13C3a (G), or bispecific anti-Aβ/anti-TfR (TBTI3a and TBTI6a) antibodies (I and K). Higher magnification views within cortical fields evidenced that remaining parenchymal Congo red-positive deposits could be decorated with IgG1 immunostaining, indicative that 13C3a (H), TBTI3a (J), and TBTI6a (L) reach their target. As expected, no IgG1 labeling was detected over Congo red-positive deposits after chronic treatment with Ctrl IgG1 antibody (F). Scale bar in the cortical insets, 50 μm.