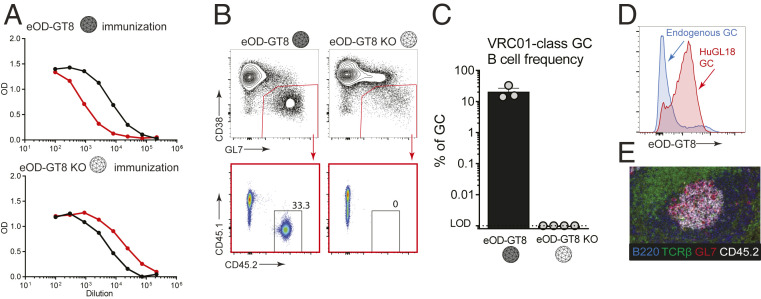
Fig. 2.
VRC01-class B cells from a BCR knockin mouse with an authentic naive human VRC01-class BCR specificity (HuGL18) can be primed and recruited to GCs. (A) Day 8 ELISA binding curves from CD45.1+ mice that received HuGL18 B cells (1 in 103 precursor frequency) and immunized with eOD-GT8 60mer (Top) or eOD-GT8-KO 60mer (Bottom). eOD-GT8 IgG titers are shown in black, KO IgG titers are shown in red. Responses are shown from individual mice that are representative of two mice per group. Bars indicate SEM. (B) Flow cytometric analysis of total BGC (gated as SSL/B220+/CD4−/CD38−/GL7+) and HuGL18 B cell occupancy of GCs (SSL/B220+/CD4−/CD38−/GL7+/CD45.1−/CD45.2+ cells) of mice immunized with eOD-GT8 60mer (Left), or eOD-GT8-KO 60mer (Right). Day 8 splenic B cells were analyzed. (C) Quantitation of VRC01-class B cells among BGC cells. (D) Flow cytometric analysis of antigen binding (eOD-GT8) by endogenous or HuGL18 BGC cells. Representative of five mice tested. Mice were immunized as in B. (E) Representative histological analysis of GCs. Frozen splenic sections were stained with B220 (blue), TCRβ (green), GL7 (red), and CD45.2 (white) for identification of HuGL18 B cells within GCs. SSL, singlet scatter live. n = 3 (B and C), n = 1 (A, D, and E). n = 3 to 4 mice per experiment.