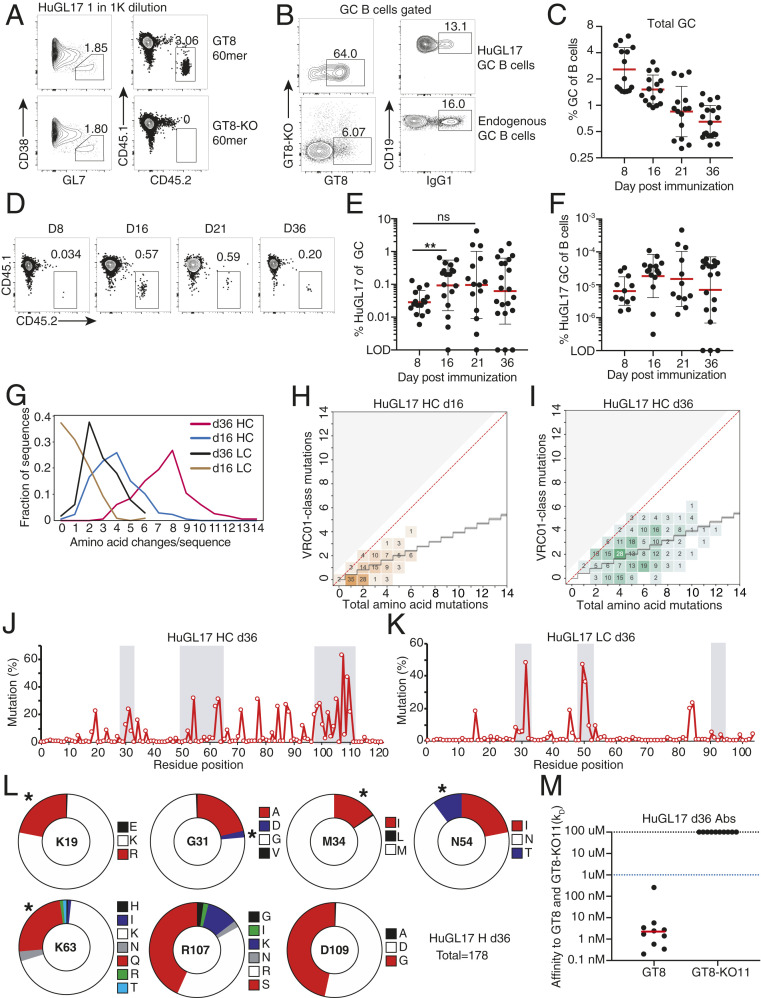
Fig. 6.
Characterization of HuGL17, a medium-affinity VK1-5+ VRC01-class BCR model. Analysis of total and HuGL17 splenic BGC cells. (A and B) Analysis of HuGL17 responsiveness to eOD-GT8 in vivo at a HuGL17 B cell precursor frequency of 10−3 (“1K” = 1,000). (A) Total (Left) and donor-derived fraction (Right, boxes) of BGC cells after immunization with eOD-GT8 or eOD-GT8-KO. (B) Representative flow plots of antigen-specific and IgG1 class-switched HuGL17 and endogenous (CD45.1+) BGC cells (TCRβ–CD19+CD38–GL7+). (C–L) Longitudinal analysis of mice immunized with eOD-GT8 60mer when HuGL17 precursor frequencies were 1 in 1 million B cells. (C) Longitudinal analysis of total frequency of BGC cells. (D) Representative flow plots enumerating HuGL17 BGC cells. (E) Longitudinal analysis of GC occupation by HuGL17 B cells. Each data point indicates the value measured in one recipient spleen. (F) HuGL17 BGC cell percent among all B cells. (G) Analysis of the number of amino acid replacements per sequence in the HC and LC, respectively, at d16 (n = 197, 172) and d36 (n = 178, 226). (H and I) Analysis of HC VRC01-class mutations on d16 and d36. Analysis was conducted as in Fig. 5D. (J and K) Distribution of replacement mutations as a function of amino acid position. (L) Quantitation of HC replacement mutations d36 (n = 178). (M) SPR measured KD affinities for mAbs recovered from paired d36 HuGL17 GC B cell sequences, with dotted blue line indicating affinity of the HuGL17 precursor. Asterisks (*) mark VRC01-class mutations. n = 3. n = 2 to 7 mice per experiment.