Figure 2.
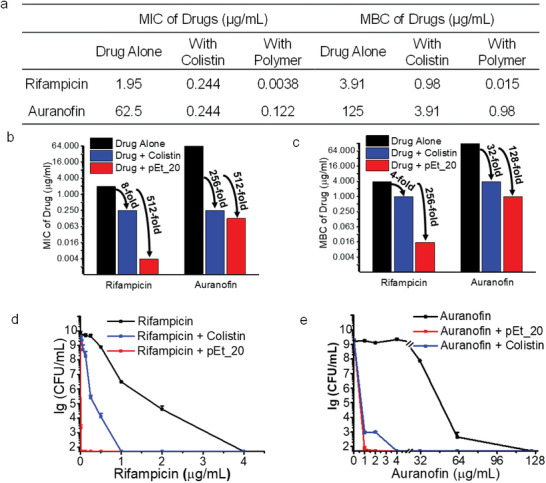
The polymer pEt_20 potentiates rifampicin and auranofin as potent antibiotics against Gram‐negative MDR A. baumannii (ATCC BAA‐1789). Rifampicin and auranofin are used in clinic for treatment of tuberculosis and rheumatoid arthritis, respectively. a) MICs and MBCs of rifampicin and auranofin with and without pEt_20. b) MIC folds reduction. c) MBC folds reduction of rifampicin and auranofin in the presence of pEt_20 in comparison with colistin sulfate. d) Killing efficiency of rifampicin and auranofin in the presence of pEt_20 in comparison with colistin sulfate. The polymer pEt_20 potentiated the antimicrobial activity of rifampicin and auranofin more effectively than colistin sulfate, leading to much greater MIC and MBC reduction (512‐ vs 8‐fold reduction in MIC and 256‐ vs 4‐fold reduction in MBC for rifampicin. 512‐ vs 256‐fold reduction in MIC and 128‐ vs 32‐fold reduction in MBC for auranofin). The pEt_20 combinations showed a stronger bactericidal effect (≥99.9% killing efficiency) than colistin sulfate. The concentration of pEt_20 and colistin sulfate: 7.8 and 0.5 µg mL−1 (0.5× MIC), respectively, at which, both pEt_20 and colistin sulfate did not kill bacteria (≈0% killing efficiency as compared to CFU at 0 h). Limit of detection: 50 CFU mL−1. MIC and MBC data are representatives of three biological replicates, and killing efficiency is presented as mean ± S.D. (n = 3).
