Figure 6.
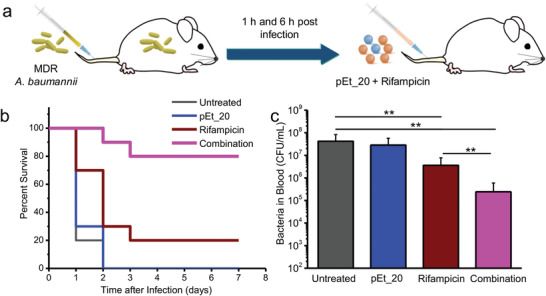
In vivo synergistic antimicrobial effects of pEt_20/rifampicin combination in a mouse bacteremia model. a) The mouse bacteremia model was created by injection of MDR A. baumannii (ATCC BAA‐1789) at 1.3 × 109 CFU mL−1 (200 µL/20 g). pEt_20 (2.0 mg kg−1) and rifampicin (5.0 mg kg−1) were sequentially injected into mouse tail vein with two doses at 1 and 6 h post infection (n = 10). b) Survival of the infected mice after different treatments. The combination therapy provided a significantly higher survival rate than monotherapy using rifampicin or pEt_20. c) Blood bacterial counts from MDR A. baumannii (6.5 × 108 CFU mL−1)‐infected mice at 24 h post infection. The combination treatment led to 2.4 log CFU reduction, which is significantly higher than rifampicin monotherapy with 1.1 log CFU reduction. (Means ± S.D. n = 6. One‐way ANOVA (Tukey's post hoc); **p < 0.01.)
