Figure 1. All forms of MMP-1 bind to LRP1 by known LRP1-mediated mechanisms.
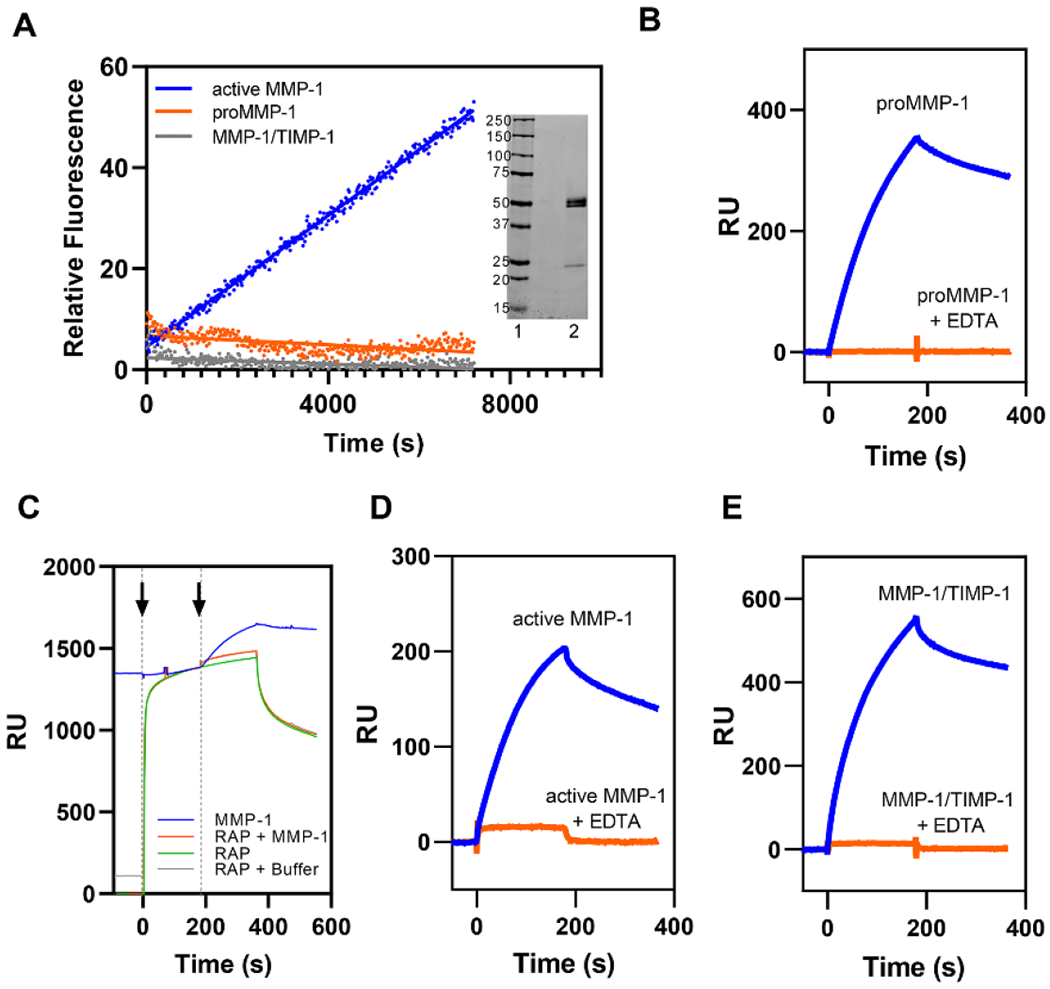
A. MMP-1/TIMP-1 complex formation abolished MMP-1 protease activity as assessed by fluorescent substrate assay. Each form of MMP-1 (20 nM) was incubated with 200 µM of quenched fluorescent substrate. Fluorescence was measured every 20 seconds for 2 hours. All measurements were controlled for by background subtraction and then the relative fluorescence intensity was averaged across all replicates (n = 3). proMMP-1 (orange), active MMP-1 (blue), and MMP-1/TIMP-1 complex (gray). Inset. SDS PAGE analysis of proMMP-1 under non-reducing conditions. Lane 1, Standards, Lane 2, proMMP-1. B. Purified LRP1 was immobilized on a CM5 sensor chip and 75 nM proMMP-1 was injected in the absence (blue lines) or presence (orange lines) of 3 mM EDTA. C. RAP (1 μM, green) was injected (first arrow) on an LRP1-coated CM5 sensor chip (green) followed by either a co-injection (second arrow) of 75 nM proMMP-1 and 1 μM RAP (orange), a co-injection of buffer and 1 μM RAP (gray), or another injection of 1 μM RAP (green). These traces were compared to an injection of 75 nM proMMP-1 (blue) in the absence of RAP. D-E. Purified LRP1 was immobilized on a CM5 sensor chip and active MMP-1 (D) or MMP-1/TIMP-1 complex (E) were injected in the absence (blue lines) or presence (orange lines) of 3 mM EDTA. The data shown is a representative experiment from three independent experiments that were performed.
