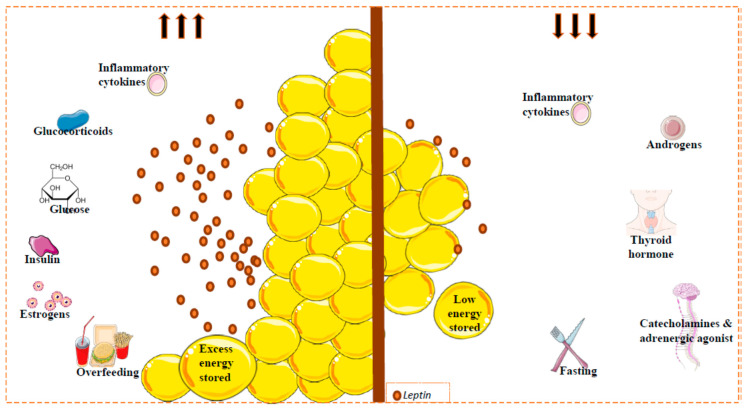
Figure 1.
Factors implicated in circulating leptin levels. Leptin is secreted mainly by white adipose tissue. Leptin levels are correlated with the amount of fat (reflecting the amount of energy stored), and with changes in caloric intake. Other factors can regulate the circulating leptin levels. Glucose, insulin, estrogens and some inflammatory cytokines (acute effect) promote leptin secretion (left); catecholamines or adrenergic agonists, thyroid hormones, androgens and inflammatory cytokines inhibit the secretion of this hormone (right). Fat mass and leptin levels are significantly affected by gender and by menopausal status, where the leptin levels can decrease; leptin levels in females are higher than in males. This sexual dimorphism is due, at least in part, to the suppressive effect of androgens on leptin [78].