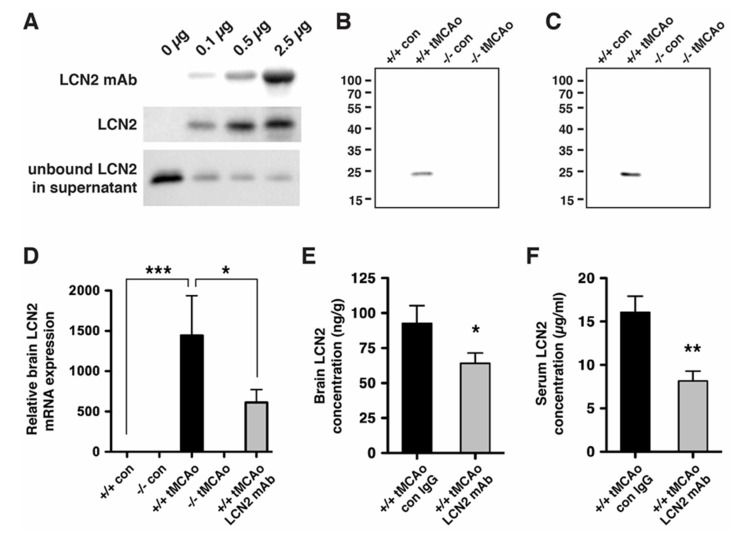
Figure 3.
LCN2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) specifically immunoprecipitated recombinant and endogenous LCN2 proteins. (A) Representative Western blots showing that LCN2 mAb reduced the level of LCN2 protein by immunoprecipitation. Increasing concentrations of LCN2 mAb (0, 0.1, 0.5, and 2.5 μg) bound to the Dynabeads were incubated with a fixed amount of mouse recombinant LCN2 protein (0.1 μg). LCN2 mAb bound to the Dynabeads, immunoprecipitated LCN2 protein, and unbound LCN2 protein in the supernatant after the immunoprecipitation are shown in the top, middle, and bottom panels, respectively; (B,C) LCN2 mAb specifically immunoprecipitated the LCN2 protein that was induced after tMCAo. Ipsilateral hemisphere lysates (B) and blood sera (C) collected from naive LCN2+/+ and LCN2−/− mice (+/+ con and −/− con) and at 23 h after tMCAo (+/+ tMCAo and −/− tMCAo) were immunoprecipitated with LCN2 mAb and analyzed by Western blotting using a polyclonal antibody that recognized LCN2 protein; (D) Total RNA isolated from ipsilateral hemispheres of naive LCN2+/+ and LCN2−/− mice (+/+ con and −/− con), at 23 h after tMCAo (+/+ tMCAo and −/− tMCAo), and LCN2+/+ mice treated with LCN2 mAb at 4 h after tMCAo (+/+ tMCAo LCN2 mAb) was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR (n = 6 per group). Relative mRNA expression of LCN2 in the brain homogenates was compared between the mice groups using a one-way ANOVA and Newman–Keuls post hoc tests. LCN2 mRNA levels were significantly induced after tMCAo (*** p < 0.001) as compared with those in naive LCN2+/+ mice. LCN2 mRNA levels in mice that were treated with LCN2 mAb were significantly reduced (* p < 0.05) as compared those in LCN2+/+ mice after tMCAo; (E,F) Mice were treated with an isotype control IgG (con) or LCN2 mAb at 4 h after tMCAo. We analyzed the concentration of LCN2 in the ipsilateral hemispheres (n = 5 per group, E) and blood sera (n = 9–10 per group, F) at 23 h after reperfusion using ELISA. The concentration of LCN2 in the brains of mice treated with LCN2 mAb were significantly decreased (* p < 0.05) as compared with that in the brains of mice that received the control IgG (one-tailed, unpaired t test). The serum concentration of LCN2 in mice that received LCN2 mAb were also significantly decreased (** p < 0.01) as compared with that in mice that received the control IgG (two-tailed, unpaired t-test).