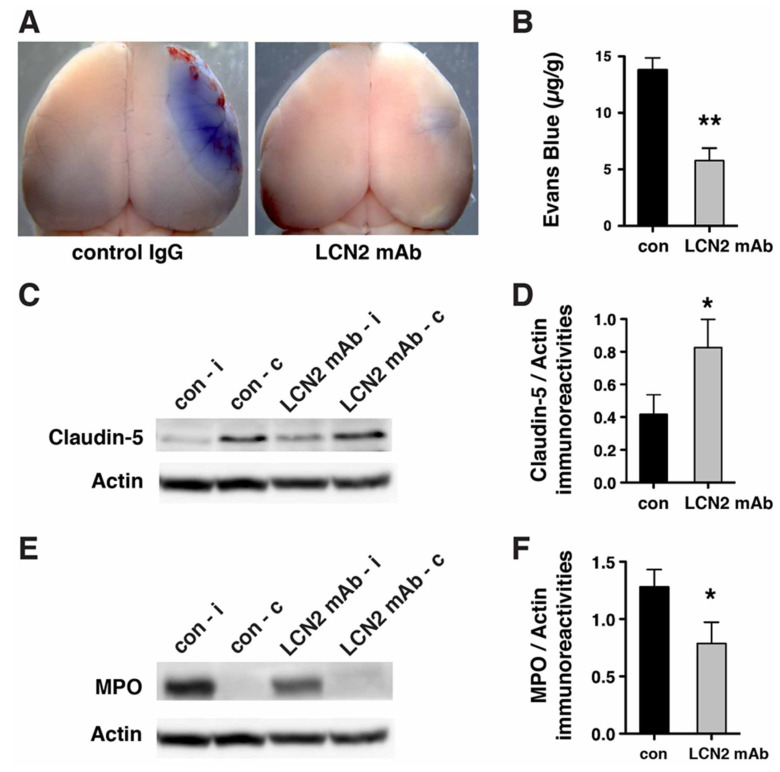
Figure 5.
LCN2 mAb limited blood–brain barrier leakage and infiltration of neutrophils after tMCAo. Representative images (A) and quantification (B) of Evans blue extravasation in the ipsilateral hemispheres of mice treated with control IgG (con) and LCN2 mAb (n = 5 per group) after one hour of tMCAo and 23 h after reperfusion. The concentration of Evans blue dye in the ipsilateral hemispheres of mice treated with LCN2 mAb was significantly decreased (** p < 0.01) as compared with that in the ipsilateral hemispheres of mice treated with control IgG (two-tailed, unpaired t test); (C) The expression level of the tight junction protein claudin-5 was analyzed after treatments with control IgG and LCN2 mAb (n = 4 per group). The ipsilateral (i) and contralateral (c) hemispheres isolated at 23 h after tMCAo were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against claudin-5. Representative Western blot showing the expression of claudin-5 (~22 kDa) in brain homogenates. β-actin served as a loading control; (D) The level of claudin-5 immunoreactivity normalized to β-actin (claudin-5/actin) in the ipsilateral hemispheres in mice treated with LCN2 mAb was significantly higher than that in the ipsilateral hemispheres of mice that received the control IgG (* p < 0.05, one-tailed, unpaired t test); (E,F) Neutrophil infiltration was analyzed by measuring the levels of MPO in brain homogenates. The ipsilateral (i) and contralateral (c) hemispheres of mice treated with control IgG (con) and LCN2 mAb (n = 4 per group) isolated at 23 h after tMCAo were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies against MPO; (E) Representative Western blots show the expression of MPO heavy chain (~55 kD) in brain homogenates; (F) The level of MPO immunoreactivity normalized to β-actin (MPO/actin) was significantly reduced in the ipsilateral hemispheres of mice treated with LCN2 mAb (* p < 0.05, one-tailed, unpaired t test) as compared with that in the ipsilateral hemisphere of mice that received control IgG.