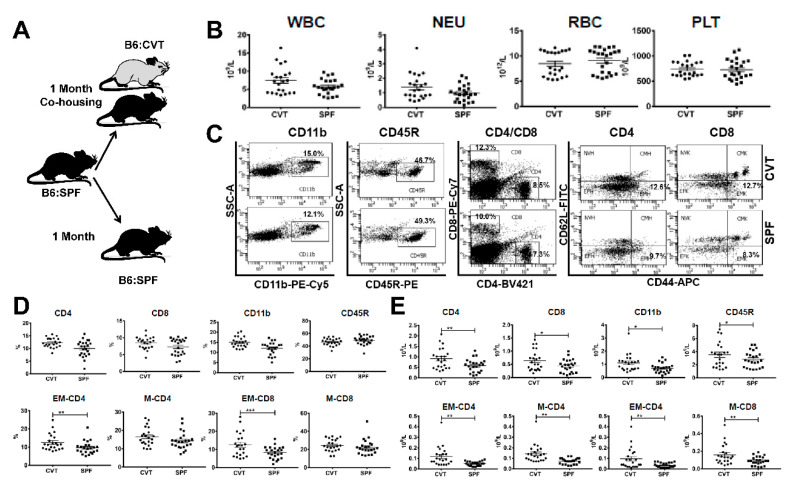
Figure 1.
(A) C57BL/6J (B6) mice born and raised in specific-pathogen-free (SPF) conditions were either maintained in SPF or transferred to a conventional facility and co-housed (CVT) with mice born and raised in that facility for one month. (B) CVT (n = 22) and SPF (n = 23) mice were bled at one month of co-housing to analyze concentrations of white blood cells (WBC), neutrophils (NEU), red blood cells (RBC) and platelets (PLT). (C) Blood leukocytes were stained with specific antibodies and were analyzed by flow cytometry for the proportions of myeloid cells (CD11b), B cells (CD45R), helper T cells (CD4), and cytotoxic T cells (CD8), while CD4 and CD8 T cells were further divided, based on expression of CD62L and CD44, into naive (NV, CD44−CD62L+), central memory (CM, CD44+CD62L+), effector (EF, CD44−CD62L−) and effector memory (EM, CD44+CD62L−) subsets, all shown as representative dot plots. (D) Proportions of CD4, CD8, CD11b, CD45R, EM-CD4, M-CD4 (memory CD4, combined CM-CD4 and EM-CD4), EM-CD8 and M-CD8 (memory CD8, combined CM-CD8 and EM-CD8) cells in peripheral blood of CVT and SPF mice. (E) Calculated concentrations of CD4, CD8, CD11b, CD45R, EM-CD4, M-CD4, EM-CD8 and M-CD8 cells in peripheral blood of CVT and SPF mice. Data were combined from two experiments performed at different times. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.