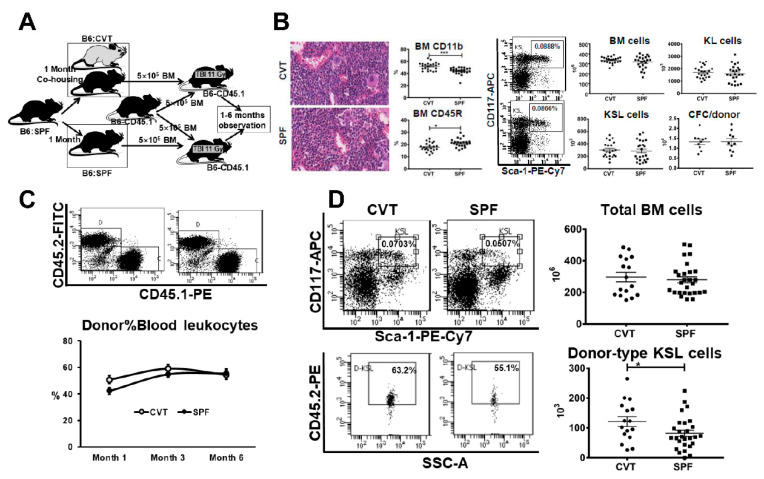
Figure 4.
(A) C57BL/6J (B6) mice born and raised in specific-pathogen-free (SPF) conditions were either maintained in SPF or transferred to a conventional facility and co-housed (CVT) with mice born and raised in that facility for one month before they were euthanized and their bone marrow (BM) cells being transplanted into lethally-irradiated B6-CD45.1 recipients through competitive repopulation in vivo. (B) CVT (n = 22) and SPF (n = 23) mice were euthanized at one month after co-housing and representative sterna from each group were examined for BM histology, while BM cells from tibiae and femurs from all animals were stained and analyzed by flow cytometry for mature CD11b and CD45R cells and immature HSPCs carrying KL (c-Kit+Lin−) and KSL (c-Kit+Sca-1+Lin−) phenotypes. Recovery of total BM cells were used to calculate recovery of KL cells, KSL cells and colony forming cells (CFC) following eight days in methylcellulose culture. (C) BM cells from CVT (n = 10) and SPF (n = 10) donors were each mixed with BM cells from young B6-CD45.1 competitors and transplanted into lethally irradiated (11 Gys) B6-CD45.1 recipients through competitive repopulation at 2-3 recipients/donor. Recipients were bled at one, three and six months to assess donor contribution. (D) Competitive repopulation recipients were euthanized at six months after transplantation and recipient BM cells were stained and analyzed for the recovery of donor-type KSL cells. Data were combined from two separate competitive repopulation experiments. * p < 0.05.