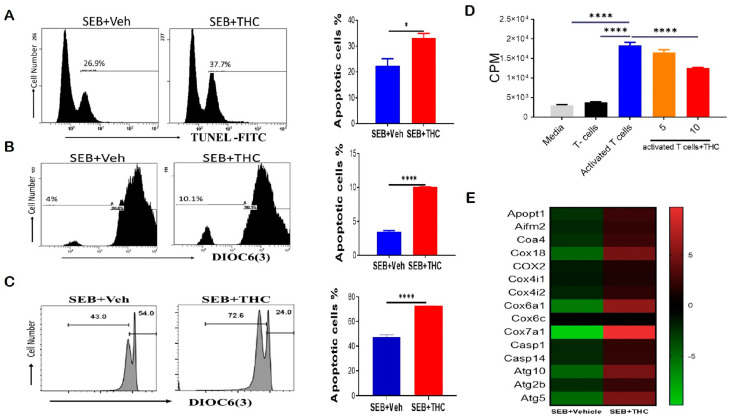
Figure 2.
THC attenuates SEB-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in mice via the induction of apoptosis. For in vivo studies, SEB-mediated ARDS was induced in C3H/HeJ mice, then the mice were treated with either Veh or THC, as described in Methods. For in vitro studies, splenocytes were isolated from naïve mice and activated in culture with SEB+Veh or SEB+THC. (A): Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling, TUNEL staining of lung mono-nuclear cells MNCs isolated from SEB+Veh and SEB+THC mice. (B): DiOC6(3) staining of CD3+ MNCs isolated from SEB+Veh and SEB+THC mice. (C): DiOC6(3) staining of CD3+ splenocytes that were activated in vitro with SEB+Veh or SEB+THC (10 uM). (D): 3H- Thymidine incorporation assay of splenocytes activated in vitro for 72 h with SEB (1µg/mL) +Veh or SEB+THC (5µm or 10µm). Thymidine incorporation is shown as counts per minute (CPM). (E): Heatmap of genes associated with apoptosis in SEB+VEH vs. SEB+THC lung MNCs. Vertical bars in panels A-C show data from 5 mice with mean+/-SEM. Statistical significance is depicted as * p < 0.05 and **** p < 0.0001 between the groups.