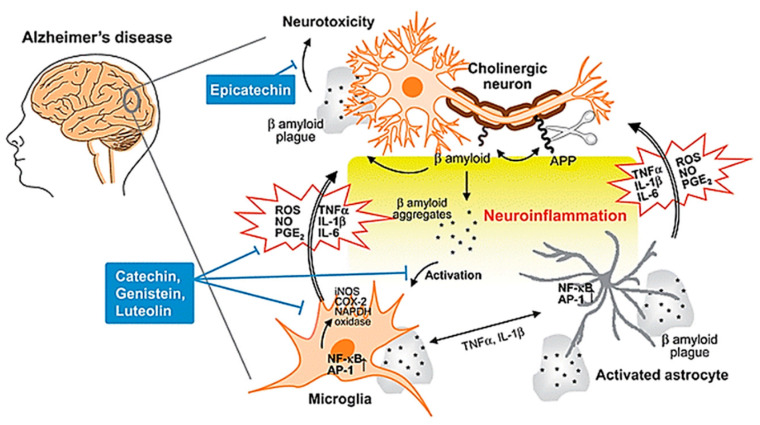
Figure 3.
Neuroinflammation in AD. During the development of AD, Aβ peptide is produced by cleavage of APP, aggregates and accumulates as β amyloid plaques. Both aggregates and plaques cause neurotoxicity or activation of microglia through up-regulating NF-κB and AP-1 transcription factors, which in turn release ROS and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as NO, PGE2, IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-a that damage cholinergic neuron. These pro-inflammatory cytokines also directly activate astrocytes that also produce cytokines to amplify inflammatory signals and result in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Flavonoids act through avoiding β amyloid induced-neuron injury and death, modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and ROS production, as well as inhibiting the activation of microglia and astrocyte as neuroprotective mechanisms. Abbreviations: AD: Alzheimer’s disease; APP: amyloid precursor protein; Aβ: amyloid beta; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa B; AP-1: activator protein 1; ROS: reactive oxygen species; NO: nitric oxide; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; IL-1: interleukin-1; IL-6: interleukin-6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor alpha. Reproduced from [30], with permission from Royal Society of Chemistry, 2010.