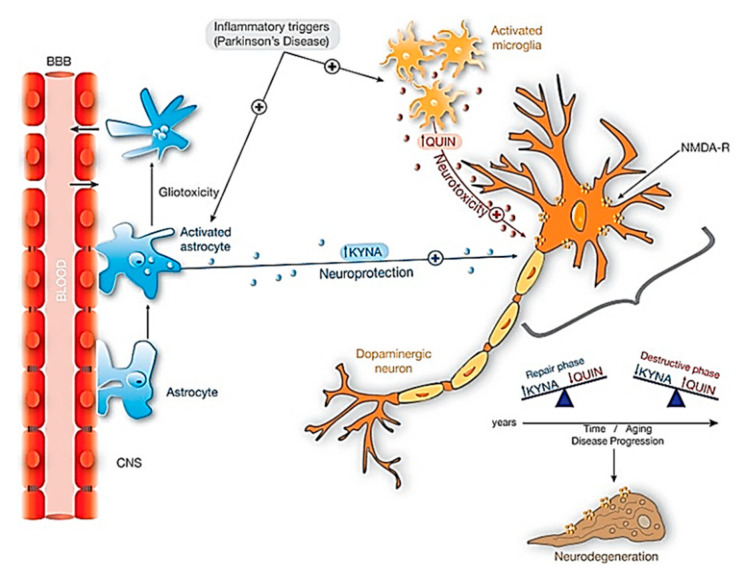
Figure 4.
Neuroprotective effects of KYNA against QUIN toxicity in dopaminergic neurons. When inflammatory triggers increased in Parkinsonism, both microglia and astrocytes activate significantly its activity. The activation of astrocytes producing KYNA is essential in this neuroprotection. Additionally, with aging and during disease progression there is an unbalance between KYNA and QUIN: in repair phases the amount of KYNA exceeds the amount of QUIN, and the contrary on the destructive phases and neurodegeneration. Abbreviations: KYNA: kynurenic acid; NMDA-R: NMDA Glutamatergic receptor; QUIN: Quinolinic acid. Reproduced from [58], with permission from Elsevier, 2017.