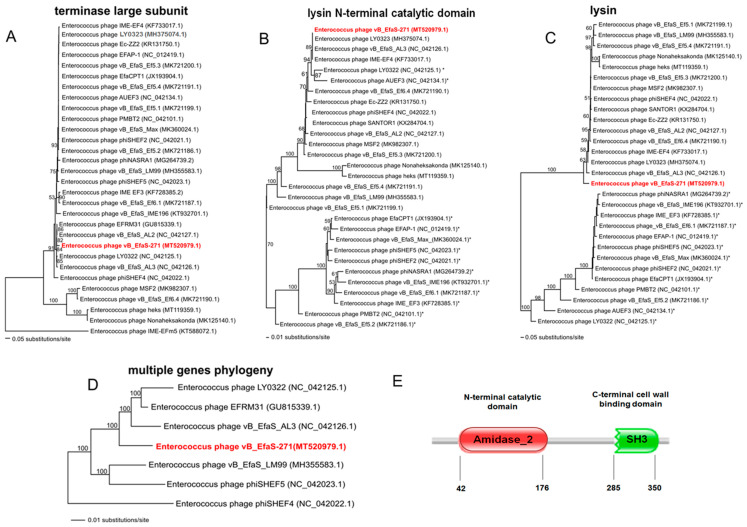
Figure 4.
Neighbour-joining phylogenetic trees showing the phylogenetic position of vB_EfaS_271 phage (in red color) across other Enterococcus phages. Trees were constructed using PAUP * and based on: the sequence coding for terminase large subunit TerL (A), fragment of the lysin gene including sequence coding for an N-terminal catalytic domain of this protein (B) the complete sequence of the lysin gene (C), and sequences of 26 genes listed in the Supplementary Table S5 and coding for proteins of known functions (D). The reference sequences of the tested genes were collected from NCBI database. Bootstrap values > 50% calculated on the basis of 1000 resamplings are shown at the nodes. Branch lengths represented by a scale bar indicate the number of substitutions per site. Panel (E) shows domain organization of the lysin protein of the vB_EfaS_271 phage. The prediction was done with the Pfam database [61] (European Molecular Biology Laboratory, ELIXIR, Pram 33.1). Available online: http://pfam.xfam.org/ (accessed on 26 August 2020). Specific protein domains: N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase (Amidase 2) and SH3 domain are marked with red and green colors, respectively. Numbers indicate positions of amino acids representing the beginning and end of the domain sequence.