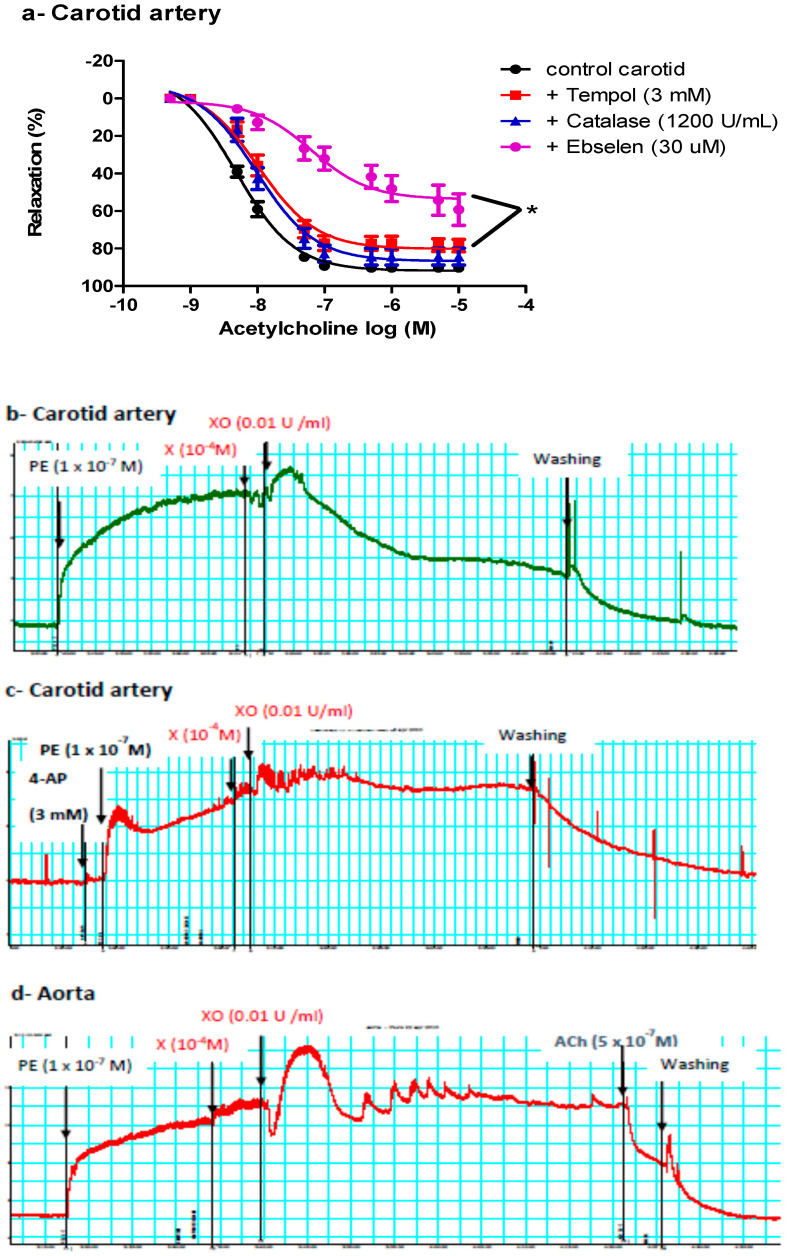
Figure 3.
Role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mediating vasodilatation in the carotid artery. (a) Cumulative concentration–response curves of acetylcholine in the carotid arteries of control and db/db mice (14–20 weeks old) in the presence or absence of tempol, catalase, or ebselen (n = 5–10 mice). (b) A representative trace showing vasodilatation after adding xanthine and xanthine oxidase to the carotid artery (n = 16 rings from six mice). (c) A representative trace showing inhibition of the vasorelaxant effect of xanthine and xanthine oxidase in the carotid artery in the presence of 4-aminopyridine (n = 4 from four mice). (d) A representative trace showing no vasodilatation after adding xanthine and xanthine oxidase to the aorta (n = 9 rings from five mice). For traces in panels b, c and d: x-axis is time (minutes) and y-axis is force (mN). 4-AP= 4-aminopyridine, Ach = acetylcholine, PE = phenylephrine, X = xanthine, XO = xanthine oxidase.