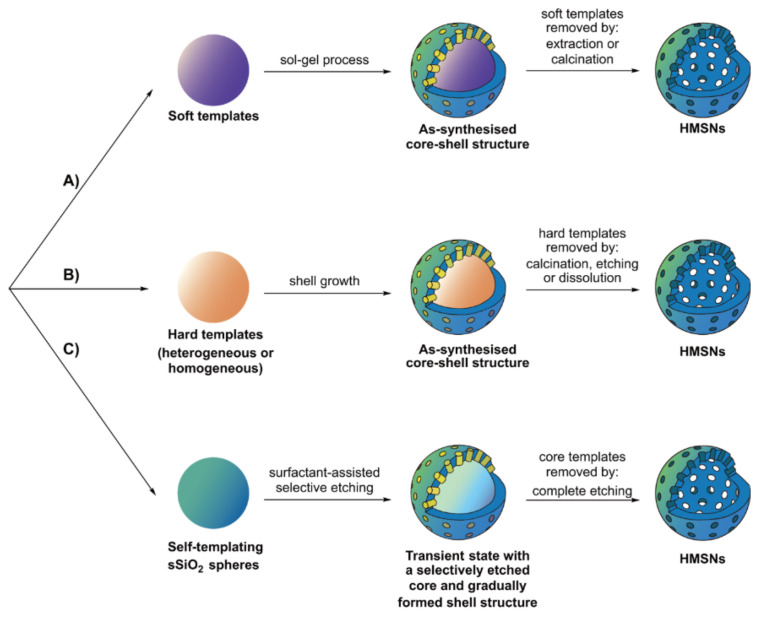
Figure 2.
A schematic detailing the three synthetic routes for fabrication of hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs), namely “soft-templating”, “hard-templating” and “self-templating”. All three routes start from the formation of the core template. Route (A) is a two-step process, resulting in the formation of HMSNs after the removal of both the mesopore and core templates. Route (B) illustrates the formation of HMSNs by a hard-templating method after the removal of both the mesopore and core templates. Route (C) shows the process of self-templating fabrication of HMSNs. The final hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles are obtained by a complete etching of self-templating solid silica spheres (sSiO2). Common etching agents include strong acids such as HCl and HF, an alkaline medium such as ammonia and NaOH, NaBH4 or hot water [49].