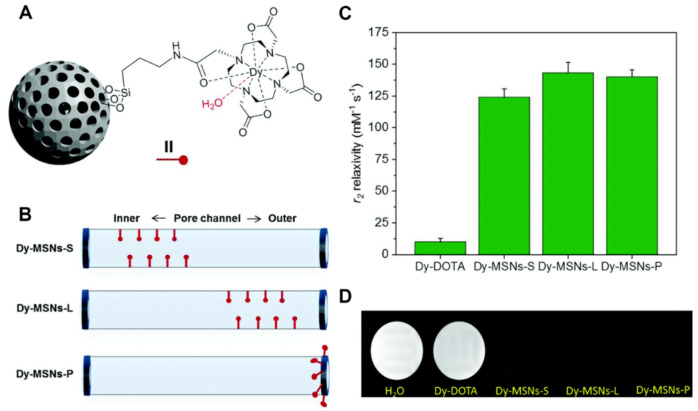
Figure 5.
A figure detailing how the position of paramagnetic chelates within MSNs affects the relaxivity (r2) values. (A) General schematic of Dy-MSNs. (B) The different available locations for the tethered Dy-chelate. S, L and P refer to the synthetic procedure i.e., short-delay, long-delay and post-grafting, respectively. (C) Associated relaxivity values where the highest relaxivity can be observed for Dy-MSNs-L with r2 = 143.5 ± 8.2 mM−1 s−1 at 11.7 T. All three locations show substantially improved r2 in comparison to native molecular Dy-DOTA. (D) MRI phantoms characterising the response of the system. Adapted with permission from reference [80]. Copyright (2018) The Royal Society of Chemistry.