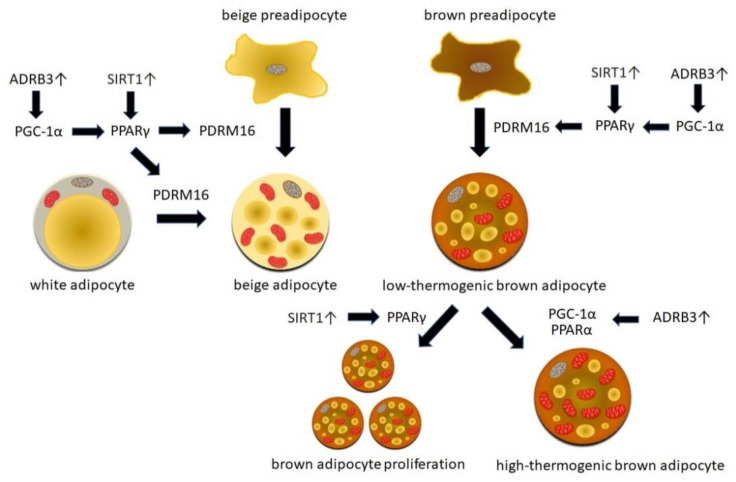
Figure 1.
Selected molecular mechanisms involved in white adipose tissue browning and brown adipose tissue activation that could constitute potential therapeutic targets for obesity treatment. Stimulation of adrenergic receptors β3 (ADRB3) is crucial for the initiation of thermogenic pathways, leading to the induction of proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) and PPARγ. Sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) also activates PPARγ and enables the recruitment of PRDM16 (PR domain containing 16) transcription factor and initiation of the brown fat specific program. These mechanisms regulate the differentiation of beige progenitors toward mature beige adipocytes and the transdifferentiation of white to beige adipocytes. Stimuli activating ADRB3 and SIRT1 are also involved in brown adipocyte differentiation, proliferation, and activation leading to the change from the low-thermogenic toward the high-thermogenic phenotype.