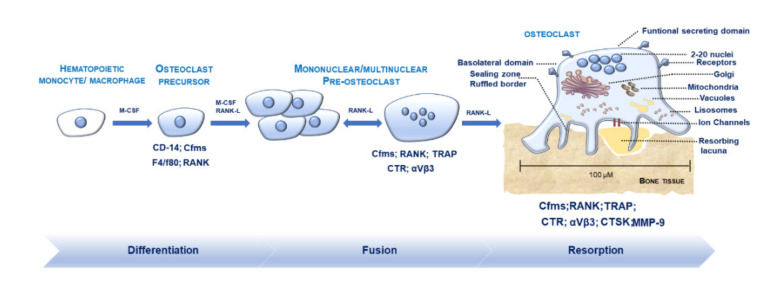
Figure 1.
Osteoclasts (OCs) formation and differentiation. Hematopoietic monocytes/macrophages mature into OCs precursors (pre-OCs) (positive for CD-14, Cfms, F4/F80, RANK) after macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) stimulation. The addition of M-CSF and receptor activator for nuclear factor κ B ligand (RANK-L) drives differentiation of pre-OCs and fusion towards mature multinucleated OCs (positive for Cfms, RANK, TRAP, CTR, CTSK, MMP-9). OCs display a polarised shape and own up to 2–20 nuclei. OCs surface membrane exhibits channels (responsible for the release of ions and matrix-degrading enzymes favouring bone resorption) and four distinct domains: the sealing zone (SZ), the ruffled border (RB), the basolateral domain (BD), and the functional secretory domain (FSD). Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, vacuoles are within the cytoplasm to support OCs function.