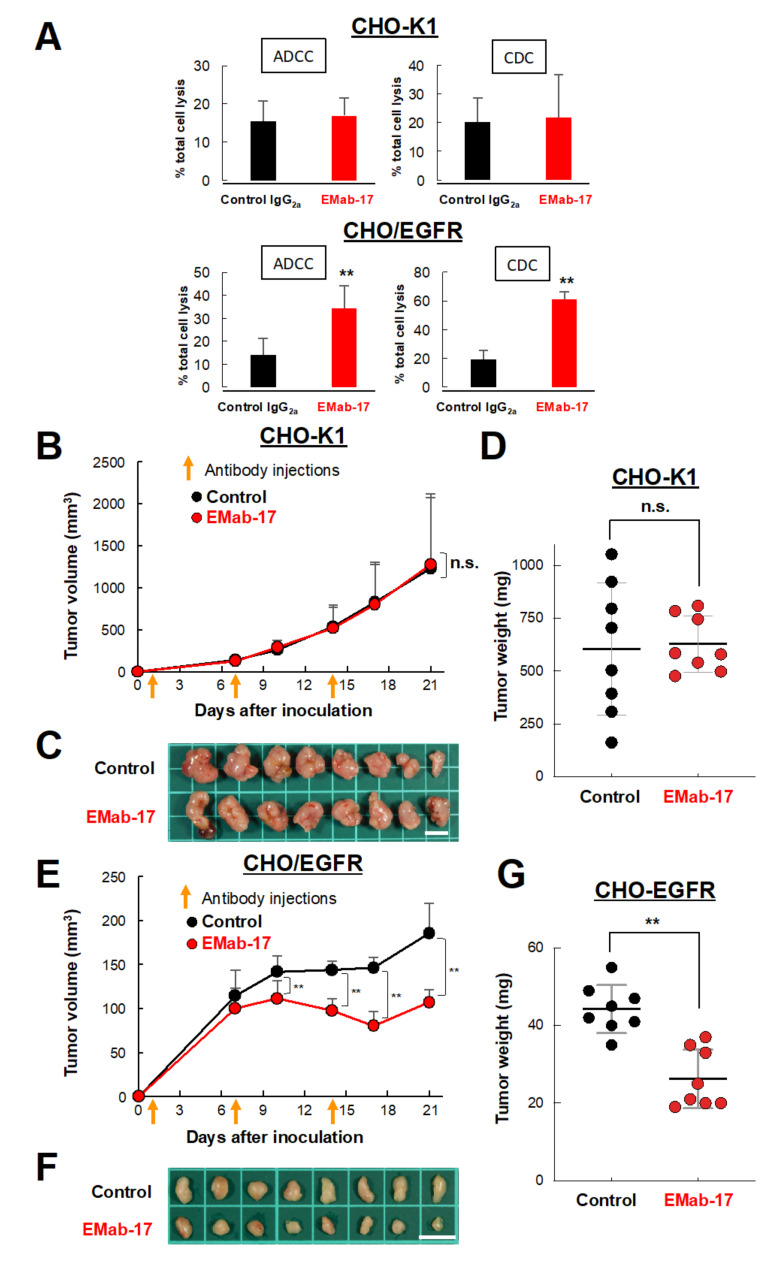
Figure 2.
Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and anti-tumor activities of EMab-17 against CHO/EGFR cells. (A) ADCC (Left) and CDC (Right) activities of EMab-17 against CHO-K1 (Top) or CHO/EGFR (Bottom) in vitro. ADCC activity was evaluated through the calcein-AM release assay in the presence of antibodies (100 μg/mL; effector/target ratio, 50). CDC activity was determined using the MTS assay in the presence of antibodies (100 μg/mL) or control mouse IgG2a (100 μg/mL) with 10% rabbit complement. **: p < 0.01 vs. IgG2a-treated control. (B, E) Anti-tumor activity of EMab-17 against CHO-K1 or CHO/EGFR cells in vivo. Tumor volume of CHO-K1 (B) or CHO/EGFR (E) xenografts. Cells (5 × 106 cells/100 μL) were subcutaneously inoculated into BALB/c nude mice. After 1 day, 100 μg of EMab-17 or control mouse IgG were injected into the peritoneal cavities of the mice. The orange arrows indicate the days of antibody injection and the antibodies were injected thrice (days 1, 7 and 14; control: n = 8; EMab-17: n = 8). The tumor diameter was measured at the indicated days and calculated using the formula: tumor volume = W2 × L/2, where W is the short diameter and L is the long diameter. Values are presented as means (SD). n.s.: not significant, **: p < 0.01 vs. control. (C, F) Resected tumors of CHO-K1 (C) or CHO/EGFR (F) xenografts on day 21. Scale bar: 10 mm. (D, G) Tumor weight of CHO-K1 (D) or CHO/EGFR (G) xenografts. Values are presented as means ± SEM. n.s.: not significant, **: p < 0.01 vs. control.