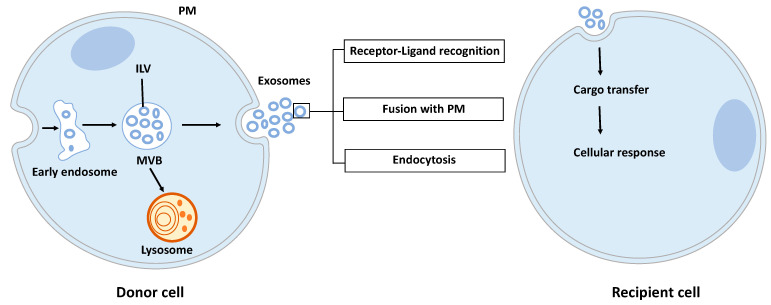
Figure 1.
Exosome biogenesis, secretion, and capture. Exosomes are formed by the inward budding of intraluminal vesicles (ILV) during the maturation of the early endosomes into the multivesicular body (MVB). ILV become exosomes after their release into the extracellular space, thus after the fusion of the MVB with the plasma membrane (PM). Released exosomes can interact with the recipient cell through receptor-ligand recognition, fusion with PM, or endocytosis. Cargo can be then transferred into the cytoplasm of the recipient cell where it can exert its effects.