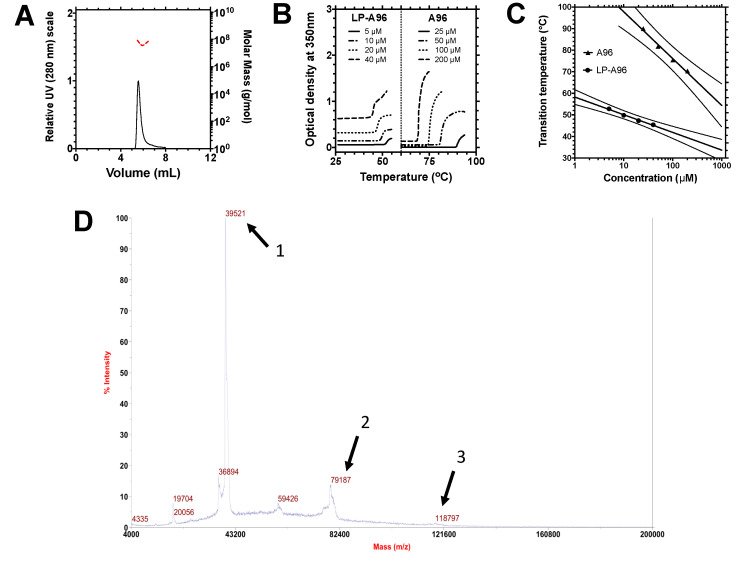
Figure A1.
Biophysical characteristics of LP-A96. (A) LP-A96 elutes from size exclusion chromatography followed by multiangle light scattering (SEC-MALS) as a single peak (solid line according to left Y-axis) consistent with a nanoparticle with a radius of gyration of 79.3 nm (red dotted line according to the right Y-axis). (B) The ELP-mediated phase separation is monitored using optical density at 350 nm as a function of temperature using UV–Vis spectrophotometry (10 μM in dPBS). ELP phase separation increases the optical density. Transition temperatures were identified using Equation (4). (C) A log-linear relationship between transition temperature and concentration was fit using Equation (3). Parameters of the fit are reported in Table A1. Dotted lines indicate 95% CI. (D) MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of LP-A96. The molecular weight of 39,521 Da (black arrow 1) is consistent with expected molecular weight reported in Table 1. Minor species identified at 79,187 Da (black arrow 2) and 118,797 Da (black arrow 3) are consistent with the masses expected for transglutaminase-mediated dimers and timers of LP-A96 [8].