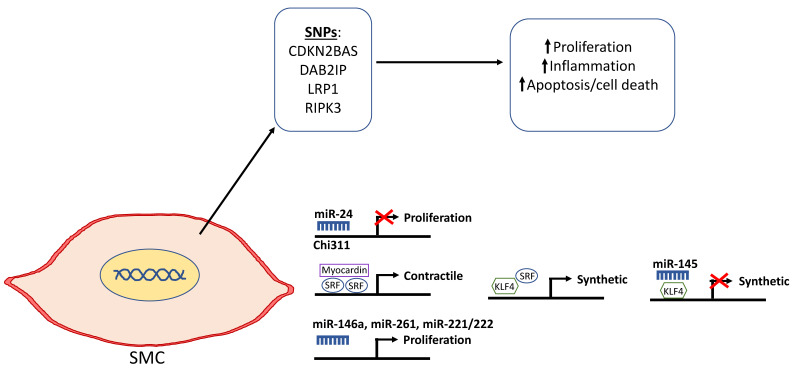
Figure 3.
Schematic depicting the genetic and epigenetic mechanisms that are involved in the phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells (SMCs) in AAA. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in selected genes including cyclin dependent kinase 2B antisense (CDKN2BAS/ANRIL), DAB2IP, lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 (LRP1), and receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (RIPK3) have been shown to be associated with the diseased SMC phenotype as depicted by increased proliferation that leads to vascular remodeling, inflammation, and cell death. miR-24 selectively targets Chi311 to inhibit proliferation. Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF4) normally represses myocardin to downregulate SMC differentiation and promote the synthetic phenotype. miR-145 can repress KLF4 and, in turn, inhibit de-differentiation into the synthetic SMC phenotype. miR-146a, miR-261, and mir-221/222 have been reported to promote SMC proliferation.