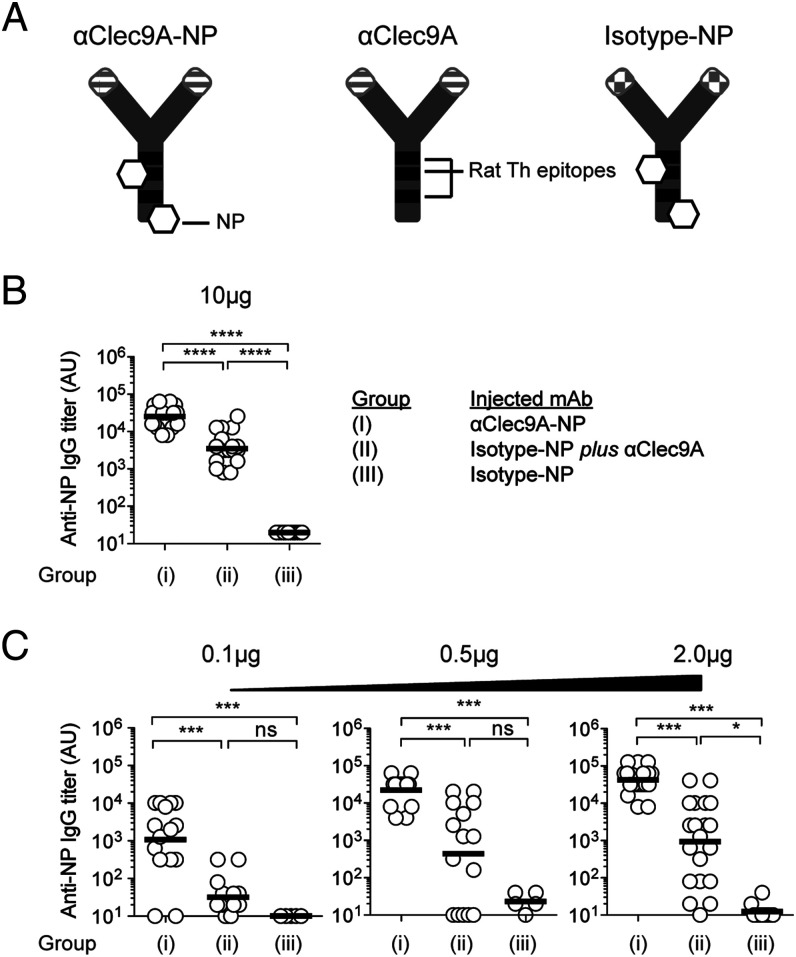
FIGURE 1.
Clec9A-mediated DC–B cell interactions promote Ab responses. (A) Diagrammatic representation of αClec9A-NP, αClec9A, and isotype-NP constructs. All three Abs are rat IgG2a and share common Th epitopes depicted as black bands. NP molecules coupled to αClec9A-NP and isotype-NP are shown as white hexagons. αClec9A-NP targets both NP and rat Ig Th epitopes to Clec9A. αClec9A only targets the rat Ig Th epitopes to cDC1. Isotype-NP does not target either NP or rat Ig Th epitopes to cDC1. (B) B6 mice were immunized i.v. with the following mixtures of Ag: group (I), 10 μg of αClec9A-NP; group (II), 10 μg of isotype-NP plus 10 μg of αClec9A; or group (III), 10 μg of isotype-NP, or (C) with lower doses of these Ag (as indicated). Anti-NP IgG titers were measured by ELISA 14 d postimmunization. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and horizontal lines indicate the geometric mean (B and C). Pooled data from four independent experiments (n = 18–20 mice per group) (B); one to three independent experiments (n = 5–15 per group) [(C), 0.1 and 0.5 μg doses] or two to four independent experiments (n = 10–20 per group) [(C), 2 μg dose]. Statistical analysis was performed on log-transformed data sets by one-way ANOVA, followed by a Tukey test (B and C). See also Supplemental Fig. 1A for SP 70 Ag. ns = p ≥ 0.05, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.