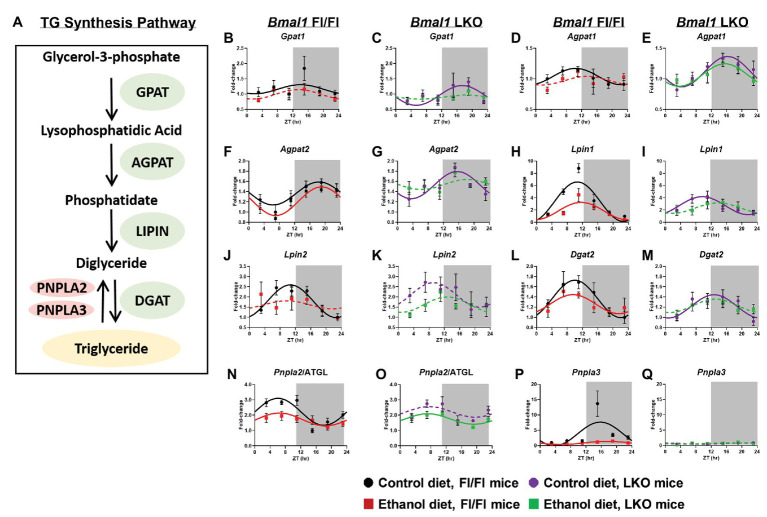
Figure 7.
Chronic alcohol and liver clock disruption alter diurnal mRNA rhythms of triglyceride metabolism genes. Pathway for triglyceride synthesis/breakdown (A). Diurnal mRNA profiles of Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase (Gpat1; B,C), 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase alpha (Agpat1; D,E), 1-acyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase beta (Agpat2; F,G), Lipin-1 (Lpin1; H,I), Lipin-2 (Lpin2; J,K), Diacylglycerol o-acyltransferase 2 (Dgat2; L,M), Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 2/Adipose Triglyceride Lipase (Pnpla2/ATGL; N,O), Patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (Pnpla3; P,Q) were measured in livers of control-fed (black) and alcohol-fed (red) Bmal1 Flox/Flox (Fl/Fl) and control-fed (purple) and alcohol-fed (green) Bmal1 liver-specific knockout (LKO) mice at ZT 3, 7, 11, 15, 19, and 23 (ZT 0: lights on/inactive period, ZT 12: lights off/active period, gray area) by RT-PCR. Data are presented as a fold-change to the Bmal1 Fl/Fl control diet trough time-point and normalized to Ppia. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM for n = 4–8 mice/genotype/diet/time point. Solid lines indicate rhythmic mRNA levels and a significant cosine fit, whereas dashed lines indicate arrhythmicity and a non-significant cosine fit. Results for Cosinor and ANOVA analyses are provided in Supplementary Tables 4 and 6, respectively.