Figure 2.
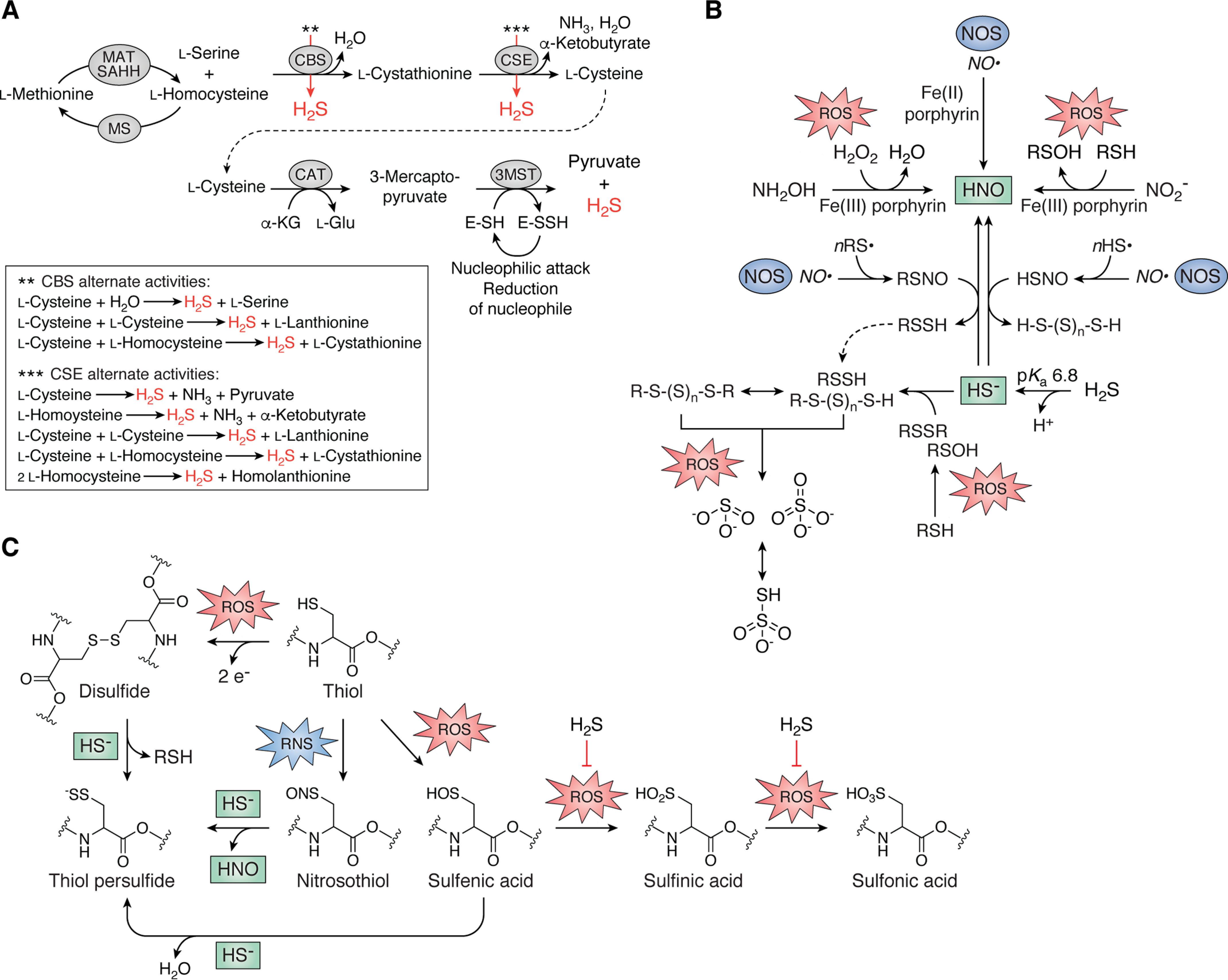
Endogenous production of H2S and cross-talk between H2S/RSS and ROS/RNS in bacteria. A, the reverse transsulfuration pathway synthesizes L-cysteine from L-homocysteine via the intermediacy of L-cystathionine, which is catabolized by CAT, whose product is utilized by 3MST to generate pyruvate and H2S (31–38). L-Homocysteine is also the immediate precursor to L-methionine. Both CBS and CSE catalyze a number of additional reactions with alternative substrates (red arrows) that generate endogenous H2S (43), illustrated in the dashed box. CBS, cystathionine-β-synthase, CSE, cystathionine-γ-lyase; MAT, methionine adenosyltransferase; MS, methionine synthase; SAHH, SAH hydrolase. B, small-molecule cross-talk between H2S/RSS and RNS and ROS. C, direct reaction of HS– with protein nitrosothiols or disulfides and sulfenic acids induced by RNS and ROS, respectively, all result in the formation of the thiol persulfide with release of HNO, protein thiol (RSH), and water, respectively. Reaction of HS– with sulfenic acids is believed to protect these protein thiols from irreversible overoxidation, indicated by the block arrow (right).
