Figure 3.
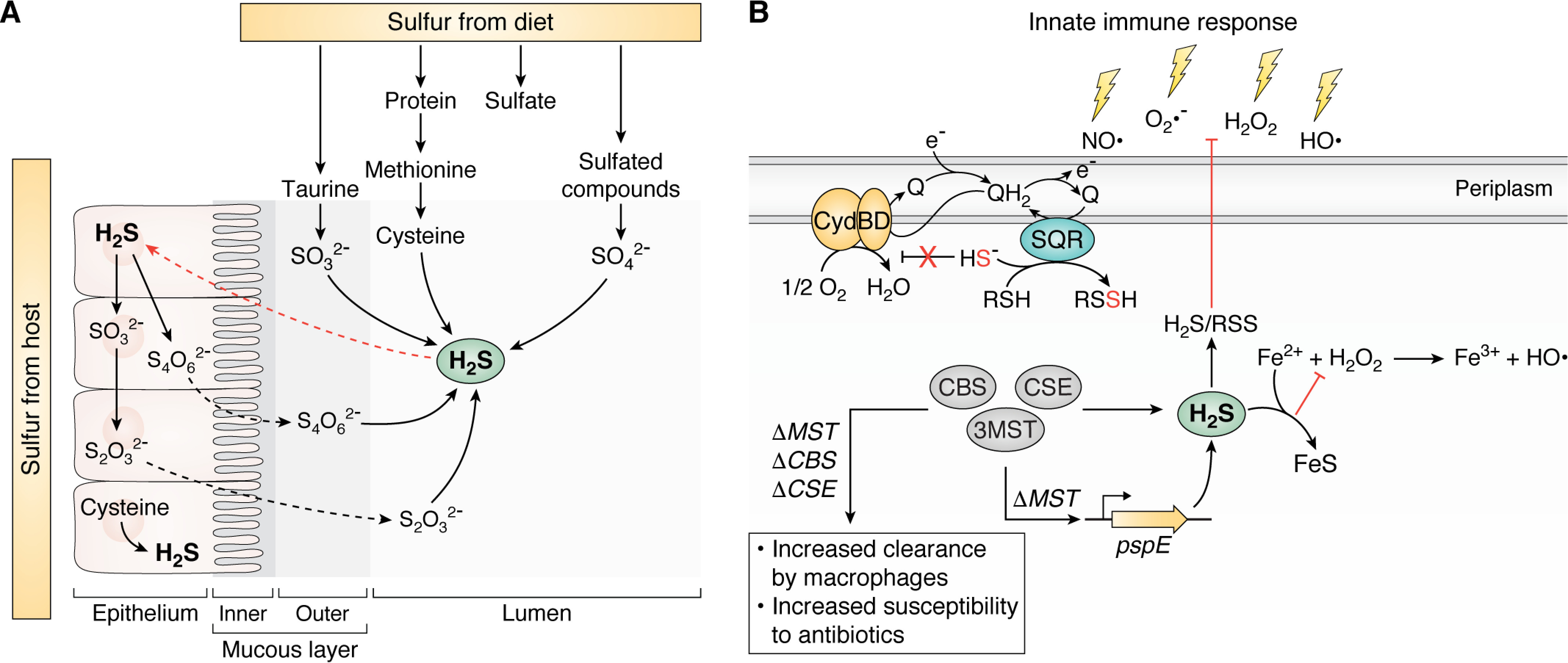
H2S and RSS at the host-pathogen interface. A, common sulfur sources in the gastrointestinal tract derived from host epithelial cells and dietary sulfur metabolized by the gut microbiota. B, endogenous production of H2S via CBS, CSE, and/or 3MST (see Fig. 2A) or other enzymatic processes and more oxidized RSS are cytoprotective against myriad stressors of innate immune response or by antibiotics. See section on physiological conditions for the production, regulation, and signaling of H2S/RSS in bacteria for details. PspE, single-domain sulfurtransferase in E. coli; Q/QH2, quinone; SQR, sulfide:quinone oxidoreductase.
