Fig. 1.
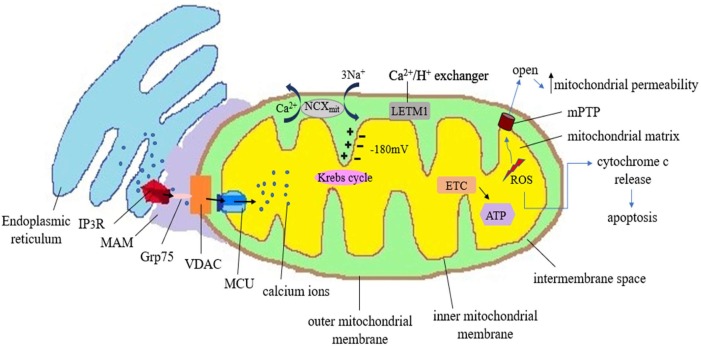
This is a schematic representation to illustrate the mitochondira-ER crosstalk and its implications in various cellular functions. ER gets tethered to mitochondria in mitochondrial associated membrane (MAM) regions which has a major role in the mobilisation of calcium ions. The inner negative potential inside the mitochondrial matrix is the thermodynamic motive due to which mitochondria can uptake cations like calcium ions. Calcium leaves ER through channels like IP3R proteins. There are some associated linker proteins in the MAM like cytoplasmic GRP75 (75-kDa glucose-regulated protein). Being a chaperone protein, GRP75 causes a link between IP3R and Voltage Dependent Anion Channel (VDAC) and facilitates calcium uptake. Calcium ions first cross outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) through gatekeeper VDAC and via tremendously selective MCU (Mitochondrial calcium uniporter), these calcium ions enter into the IMM (Inner Mitochondrial Membrane). Complexes I and III of respiratory chain generate ROS as by-products in the mitochondria. When a certain threshold level is crossed, mitochondrial calcium can promote oxidative stress. As mitochondrial permeability transition pore (mPTP) opens, there is significant increase in membrane permeability which is detrimental to cell. Such direct and indirect increase in the oxidative stress promotes the release of cytochrome c to initiate the apoptosis. Mitochondria have some ion exchanger anti-porters that help to regulate the level of calcium and homeostasis. Na2+ /Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) uses the energy of electrochemical gradient of mitochondria and cause efflux of calcium ion in exchange of sodium ions. Leucine Zipper And EF-Hand Containing Transmembrane Protein 1 (LETM1), a proton calcium exchanger, also has a role in regulating the level of calcium ions inside the mitochondria.