Figure 1.
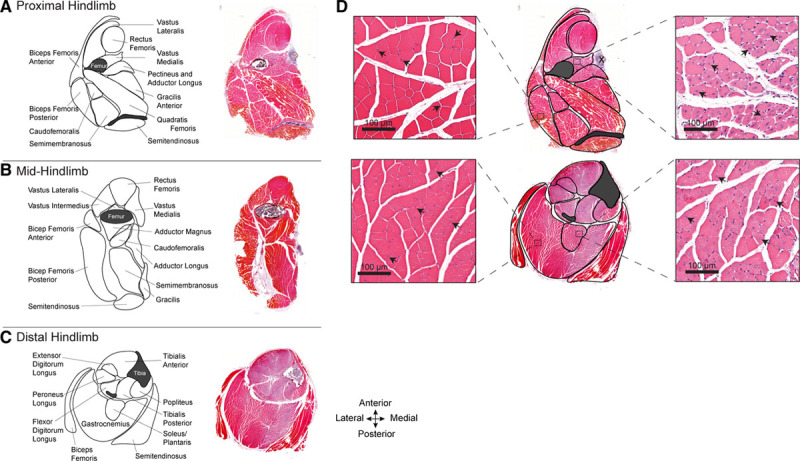
Atlas of the hind limb skeletal muscles of C57BL/6J mice subjected to femoral artery excision. A–C, Maps depicting the skeletal muscles in the proximal (A), mid- (B), and distal mouse hind limb (C). Adjacent to each map is a corresponding hematoxylin and eosin–stained full cross section of the hind limb, 10 d after femoral artery excision. Varying intensities of muscle eosinophilia can be seen; less intense staining is present in territories of ischemic injury. D, High-magnification images, corresponding to the outlined zones within the proximal and distal hind limb, depicting normal (left) and injured (right) regions of the same muscle sections. The uninjured regions have peripheral myofiber nuclei (arrowheads). The injured/regenerating regions have pale myofibers with centralized nuclei (arrowheads).
