Figure 2.
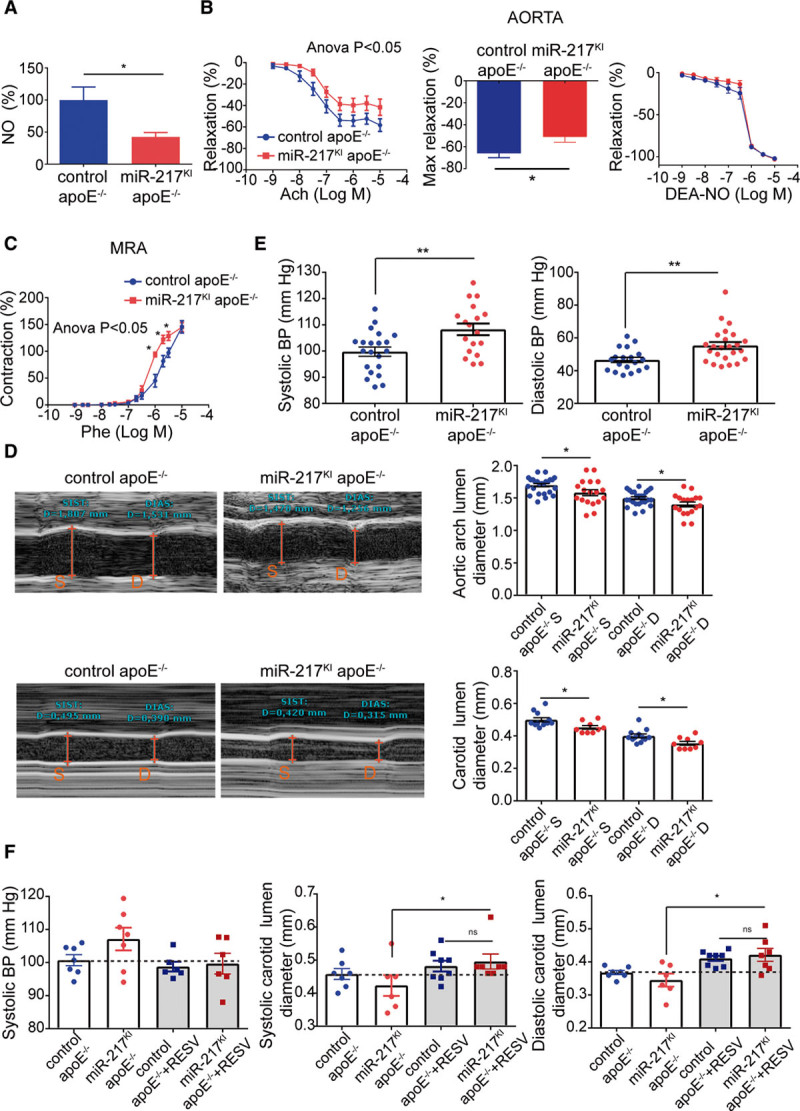
miR-217 expression impairs endothelial physiology. A, Acetylcholine (ACh)-induced NO production in aortas from male control apoE−/− mice (miR-217+/+ VE-Cad CreERT2TG/+ apoE−/−) and miR-217KI apoE−/− mice (miR-217KI/+ VE-Cad CreERT2TG/+ apoE−/−) fed with HFD for 12 wk. B, Concentration-response curves to ACh or the NO donor diethylamine NONOate (DEA-NO) and maximal relaxation to ACh of aorta from male control apoE−/− mice and miR-217KI apoE−/− mice. C, Concentration-response curve to phenylephrine (Phe) of mesenteric resistance arteries, from male control apoE−/− mice and miR-217KI apoE−/− mice. *P<0.05 vs control apoE−/− mice by 2-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test. Maximal relaxation was analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test. D, Echocardiography assessment of systolic (S) and diastolic (D) aortic arch lumen diameter (top) and right carotid lumen diameter (bottom) in control and miR-217 apoE KO (knockout) mice fed with HFD for 12 wk. E, Systolic and diastolic blood pressure (BP) in control apoE−/− and miR-217KI apoE−/− mice fed with HFD for 10 to 11 wk. F, BP and carotid diameters in control apoE−/− and miR-217KI apoE−/− mice fed an HFD before and 1 wk after resveratrol (RESV) administration. Each dot represents an individual mouse. Systolic BP unpaired t test P (miR-217KI apoE−/− vs control apoE−/−+resveratrol P=0.059; miR-217KI apoE−/− vs miR-217KI apoE−/−+resveratrol P=0.14; control apoE−/−+resveratrol vs miR-217KI apoE−/−+resveratrol P=0.8) *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ns (not significant) by unpaired t test (A–E). *P<0.05 by paired t test (F). apoE indicates apolipoprotein E; and MRA, mesenteric resistance arteries.
