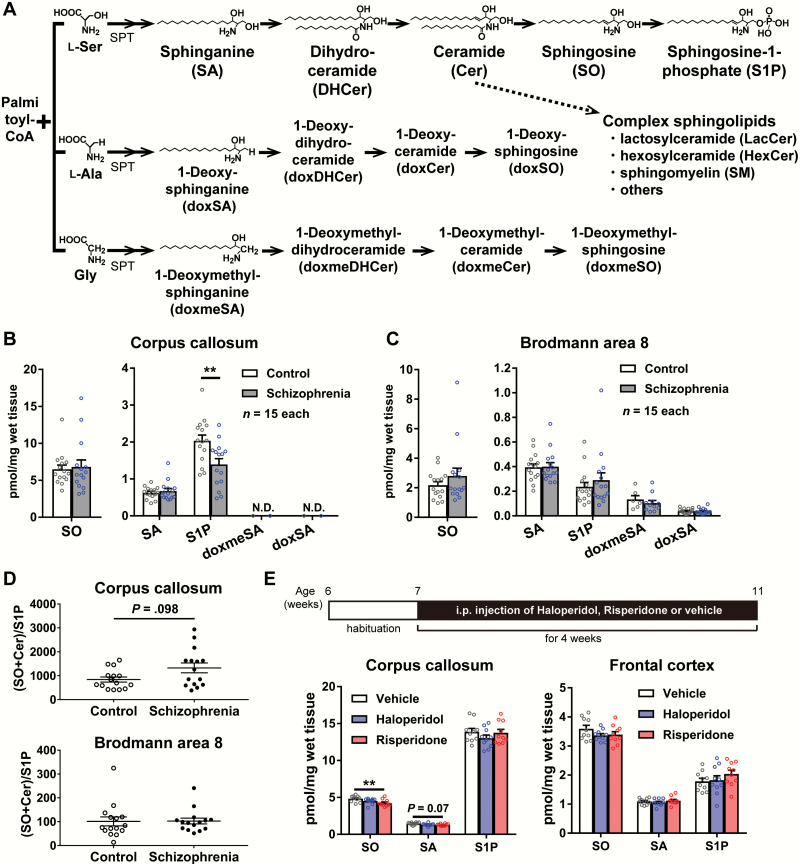
Fig. 1.
Sphingoid base levels in postmortem human and mouse brains. (A) Sphingolipid synthesis pathway. Sphingolipid biosynthesis starts with the condensation of palmitoyl-CoA and l-serine by serine palmitoyltransferase (SPT). Then, sphinganine (SA), dihydroceramide (DHCer), ceramide (Cer), sphingosine (SO), and sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) are serially synthesized. Furthermore, not only l-serine (Ser) but also l-alanine (Ala) or glycine (Gly) is used to generate sphingoid bases. Lipids were analyzed for sphingoid base levels from (B) the corpus callosum and (C) Brodmann area 8. S1P levels are low in the corpus callosum of patients with schizophrenia. The levels of doxSO and doxmeSO are below the detection limits in the corpus callosum and BA8, limiting their quantification. (D) The ratio of the sum of SO and Cer to S1P in the human corpus callosum and Brodmann area 8. (B–D) Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. N.D., not determined; **P < .01. Differences between 2 groups were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test. (E) Administration of antipsychotic drugs did not affect S1P levels in the corpus callosum and frontal cortex of mice. Data are represented as the mean ± SEM. **P < .01. Differences among 3 groups were analyzed by non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis analysis, followed by Dunnett’s test (vs vehicle group).