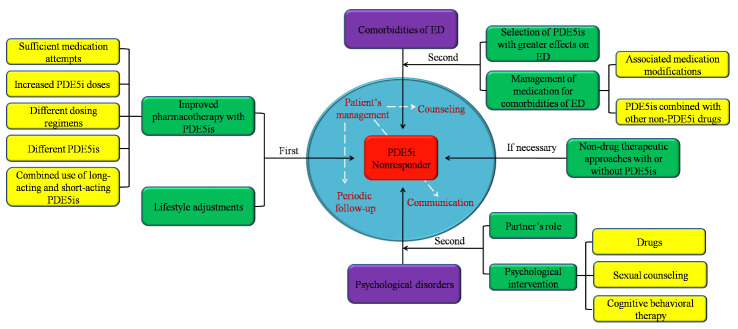
Figure 2.
Management of strategies to treat ED in PDE5i nonresponders. In the management of PDE5i nonresponders, the first-line strategies consist of lifestyle adjustments and improved pharmacotherapy with PDE5is, including sufficient medication attempts, increased PDE5i doses, different dosing regimens, different PDE5is and the combined use of long-acting and short-acting PDE5is. If the patient has an obvious mental disorder, we should focus on the patient’s psychology and give corresponding treatment, such as attaching importance to the partner’s role and providing psychological intervention, including drugs, sexual counseling and cognitive behavioral therapy. In addition, strategies of improved pharmacotherapy with PDE5is and lifestyle adjustments should be added. If ED patients have comorbidities, comorbidity-related strategies, such as the selection of PDE5is with greater effects on ED and the management of medications for comorbidities of ED, including associated medication modifications, and combining PDE5is with other non-PDE5i drugs, should be fully considered on the basis of the strategies of improved pharmacotherapy with PDE5is and lifestyle adjustments. If necessary, non-drug therapeutic approaches with or without PDE5is can be selected according to the actual treatment profile of each PDE5i nonresponder. It is worth noting that in process of treating every PDE5i nonresponder, patient management should be of great concern. Periodic follow-up visits should be carried out to find any deficiencies in the ED treatment process. Good communication should also be established through patient counseling to resolve patients' concerns and ensure the smooth implementation of treatment.