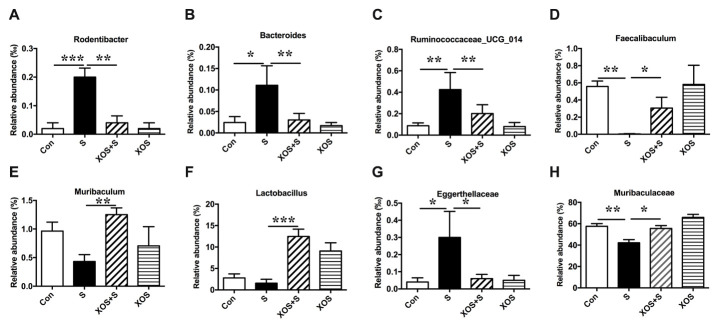
Figure 4.
XOS intervention attenuated intestinal microbiota alteration induced by surgery Chart of the relative abundance of the differential levels of bacteria at the genus and family level. (A-C) Three genera (Rodentibacter, Bacteroides, Ruminococcaceae_UCG_014) were increased in S group compared with Con group, and XOS intervention attenuated the increase of these three genera after surgery. (D) One genus (Faecalibaculum) was decreased in S group compared with Con group, and XOS intervention attenuated the decrease of this genus after surgery. (E and F) Two genus (Muribaculum and Lactobacillus) were increased in XOS+S group compared with S group. (G) One family (Eggerthellaceae) was increased in S group compared with Con group, and XOS intervention attenuated the decrease of this genus after surgery. (H) One family (Muribaculaceae) was decreased in S group compared with Con group, and XOS intervention attenuated the decrease of this genus after surgery. Results were presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). Two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni test, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.