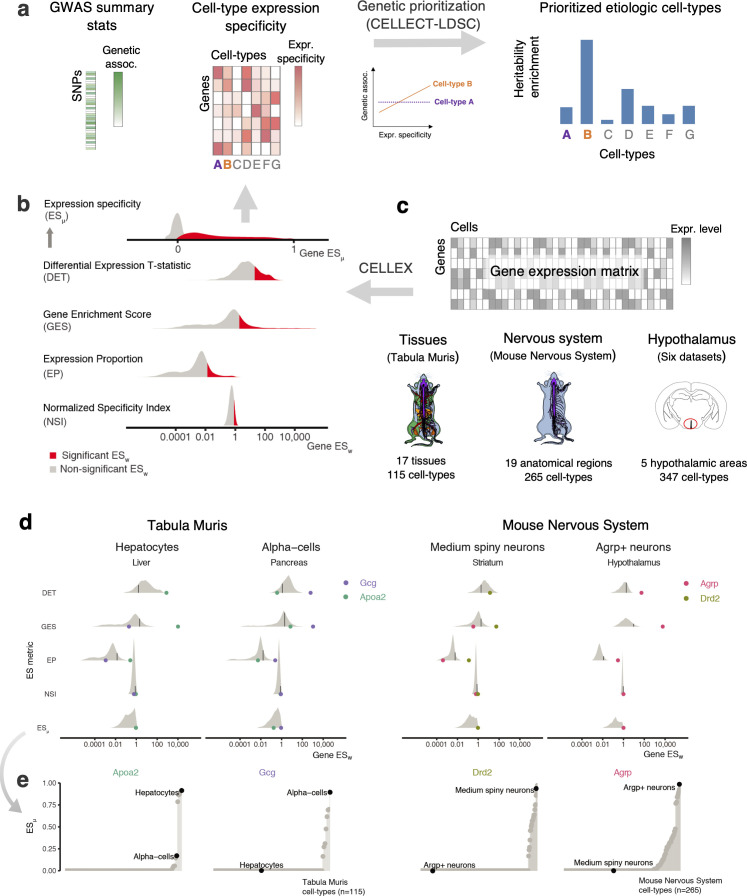
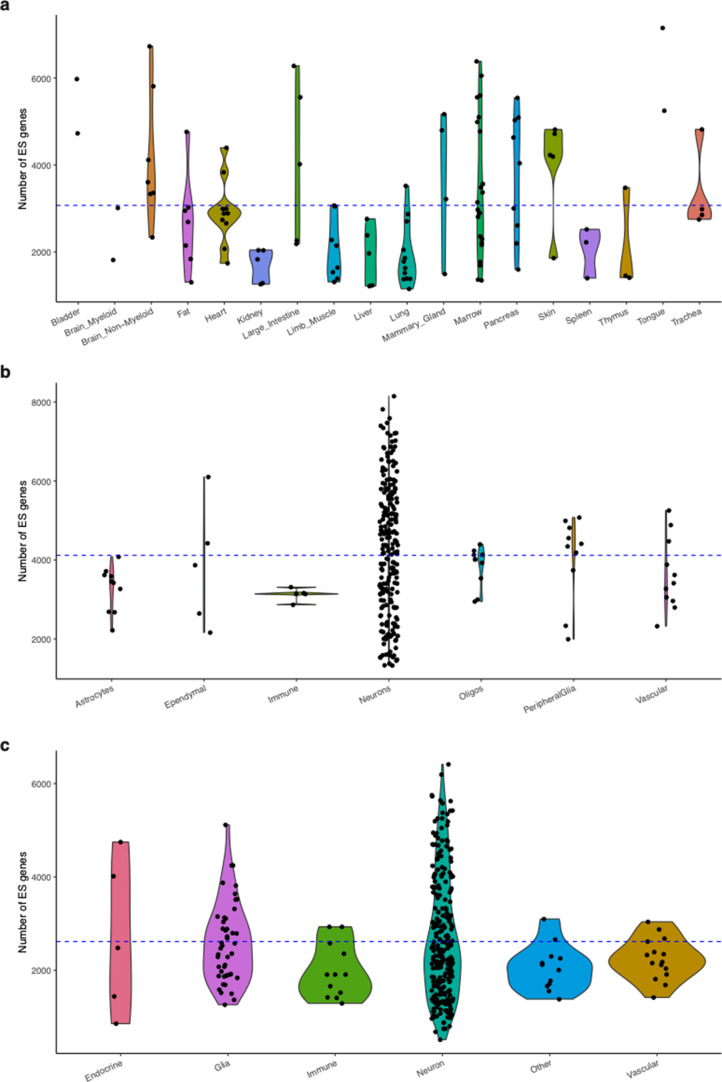
Figure 1. Overview of CELLECT and CELLEX and main datasets used (a) CELLECT quantifies the association between common polygenetic GWAS signal (heritability) and cell type expression specificity (ES) to prioritize relevant etiological cell types.
As input to CELLECT, we used BMI GWAS summary statistics derived from analysis of UK Biobank data (N > 457,000 individuals) and ES was calculated using CELLEX. (b) CELLEX uses a ‘wisdom of the crowd’ approach by averaging multiple ES metrics into ESμ, a robust ES measure that captures multiple aspects of expression specificity. Prior to averaging ES metrics, CELLEX determines the significance of individual ES metric estimates (ESw), indicated by the red and gray colored areas. (c) scRNA-seq datasets analyzed in this study. In total, the associations between 727 cell types and BMI heritability were analyzed. Anatograms modified from gganatogram (Maag, 2018). (d) Example of the CELLEX approach for selected cell types and relevant marker genes. The log-scale distribution plot of ESw illustrate differences of ES metrics. For each ES metric distribution, a black line is shown to indicate the cut-off value for ESw significance. In most cases, the ES metrics identified the relevant marker gene as having a significant ESw. In all cases, the marker gene was correctly estimated as having ESμ~1. We note that the majority of genes have ESμ=0 and were omitted from the log-scale plot. (e) ESμ plots showing the specificity and sensitivity of our approach. The plots depict ESμ for the genes shown in panel (d) across all cell types in the respective datasets. For each marker gene, the relevant cell type has the highest ESμ estimate (high sensitivity) and cell types in which the given gene is likely to have a lesser role have near zero ESμ estimates (high specificity). BMI, body mass index; ES, expression specificity; GWAS, genome-wide association study; UK, United Kingdom; scRNA-seq, single-cell RNA-sequencing.