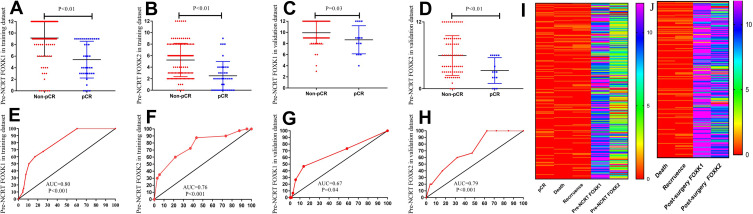
Figure 3.
Association of pre-NCRT FOXK1, FOXK2 expression with pCR. (A–D) the expression of FOXK family were lower in the pCR group compared with the non-pCR group in the training dataset (FOXK1, 9.15±0.28 vs. 5.40±0.50, P<0.01; FOXK2. 5.25±0.39 vs. 2.50±0.39, P<0.01) and validation dataset (FOXK1, 9.93±0.24 vs. 8.67±0.65, P=0.03; FOXK2. 5.96±0.42 vs. 3.27±0.60, P<0.01). (E–H) ROC analysis demonstrated that both FOXK1 and FOXK2 have a powerful ability to predict pCR in the training dataset (FOXK1, AUC=0.80, P<0.01; FOXK2, AUC=0.76, P<0.01; (E and F) and the training dataset (FOXK1, AUC=0.67, P=0.04; FOXK2, AUC=0.79, P<0.01). (I) the immunohistochemical analysis score of the pre-NCRT FOXK1 and FOXK2 expression. (J) the immunohistochemical analysis score of the post-surgery FOXK1 and FOXK2 expression.